Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
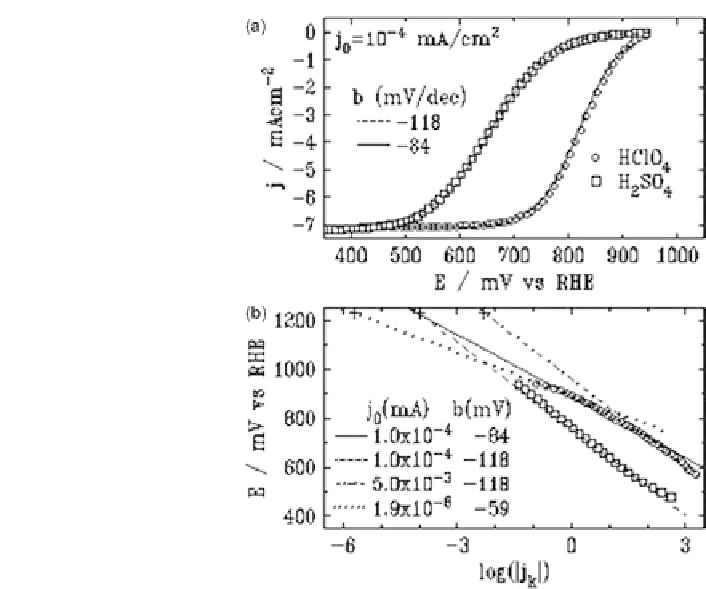
Figure 9.4 (a) Rotating disk electrode polarization curves for ORR on Pt(111) at 2500 rev/
min with a sweep rate of 50 mV/s in oxygen-saturated 0.1 M HClO
4
(circles) and 0.05 M
H
2
SO
4
(squares) solution, obtained by averaging the absolute currents in both positive and nega-
tive sweep directions. The solid and dashed lines are fitted curves using j
k
in (9.2). (b) The Tafel
plots for the data in (a), with the straight lines corresponding to different Tafel slopes and
exchange currents. (Reproduced with permission from Wang et al. [2004].)
coverage-dependent potential shift, 21u, through the exponential term, where gand 1
are the site-blocking and energy coefficients for either OH or the bisulfate anion (rep-
resented by OH and A, respectively) and m is the number of Pt sites involved in the
rate-determining step. The potential-dependent coverages u
OH
(E) and u
A
(E)
were obtained by integrating the currents measured by linear sweep voltammetry in
nitrogen-saturated solutions. Very good fitting of the experimental curves was
obtained (Fig. 9.4).
The relevance of Pt - OH formation to the change in the Tafel slope has been
demonstrated by varying the content of water in the electrolyte [Murthi et al.,
2004]. The experiments were performed in H
2
O/trifluoromethanesulfonic acid
(TFMSA) mixtures with several water/acid molar ratios. Whereas at high water con-
tents the usual change in the Tafel slope from 2112 to 259 mV/dec observed in aqu-
eous solutions of H
2
SO
4
and HClO
4
took place, at low water contents no change in the
Tafel slope was observed. This corroborates the involvement of water in the formation






Search WWH ::

Custom Search