Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 8.5
LEIS spectra for ZnAl
2
O
4
(solid line) and ZnO (dashed line) obtained with a
3 keV He
þ
beam.
(Reprinted
with
permission
from
Brongersma
and
Jacobs
[1994].
Copyright 1999. The American Physical Society.)
or Ar
þ
) with energies between 0.5 and 3 keV. The energy of the scattered ions is in
direct correlation with the mass of the target atoms, and therefore can be interpreted
as a “mass spectrum” of the surface.
Figure 8.5 shows the LEIS spectra of ZnAl
2
O
4
and ZnO as a characteristic example
of a multicomponent system analyzed by this technique [Brongersma and Jacobs,
1994]. Since only the surface peaks of Al and O were detected for ZnAl
2
O
4
, the Zn
atoms must be located in the subsurface layers. The onset of the tail agrees between
the spectra, indicating that Zn is present in the second and deeper layers. This example
illustrates the strength of the LEIS technique, in that characteristic peaks from different
elements can be used to selectively analyze the atomic composition of the topmost
surface. In addition, the shape of the tails could provide information on the in-depth
distribution of the elements.
This has been used, for instance, to follow the formation of palladium silicide in a
silicon wafer for thicknesses up to 6 nm [Vanleerdam et al., 1990]. More recently,
investigation of the tails in LEIS has been used as a tool for high resolution nondes-
tructive in-depth composition analysis of ultrathin layers [Brongersma et al., 2003]
and shallow interfaces [Janssen et al., 2004].
Although it is, in principle, feasible to quantify LEIS results, the determination of
absolute ion fractions is far from trivial. In LEIS experiments, the surface composition
is therefore generally obtained in a relative measurement by comparison of signals of
the element in the sample of interest with those of reference samples, assuming that the
matrix does not have a significant role and that the surface roughness is similar.
8.2.4 Chemical Nature of Metal -Electrolyte Interfaces
In addition to the structure and composition of the electrode, evaluation of an electro-
chemical interface in terms of the nature of adsorbates has long been recognized as a




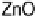




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search