Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
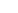
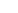
Figure 8.4 STM images (100 nm
100 nm size) of Pt(111) covered by CO for (a) as-prepared
electrode and (b) CO-annealed electrode (20 consecutive cycles) to 0.95 V. The images (U
tip
¼
0.15 V; I
tip
¼ 1 nA) illustrate the presence of islands and steps on the surface.
For instance, in our laboratory, we have recently successfully coupled ex situ STM
experiments with electrochemical treatment of Pt single crystals, and we have been
able to assign certain changes in surface morphology to electrochemical pretreatment
[Strmcnik et al., 2008].
The image of the as-prepared Pt(111) electrode (Fig. 8.4a) reveals that the surface is
composed of a flat terrace that is covered by a small number of ad-islands with mon-
atomic height. These features are even more evident on the as-prepared Pt(100) elec-
trode [Strmcnik et al., 2008]. The origin of such islands is likely due to lifting of
reconstructions in the thermally annealed surfaces. However, after CO annealing to
0.95 V [Arenz et al., 2005], i.e., cycling the potential in the CO saturated electrolyte,
the ad-islands completely disappear (Fig. 8.4b) and are replaced by a series of smooth
terrace - step structures. Since this transformation only occurs above the ignition
potential for CO oxidation, conclusion is that the CO oxidation reaction, as opposed
to simple CO adsorption, leads to step formation on the surface. Both surface features
can have a dramatic influence on catalytic activity, since the topmost atoms have
different coordination numbers in each case [Strmcnik et al., 2008; Arenz et al.,
2005; Lebedeva et al., 2002]. This illustrative example emphasizes the capability of
STM in the characterization and control of the active sites.
8.2.3 Surface Composition
Another very important technique for fundamental consideration of multicomponent
systems is low energy ion scattering (LEIS) [Taglauer and Heiland, 1980; Brongersma
et al., 2007]. This is a unique tool in surface analysis, since it provides the ability to
define the atomic composition of the topmost surface layer under UHV conditions.
The signal does not interfere with the subsurface atomic layers, and therefore the
results of LEIS analysis represent exclusively the response from the outer surface.
In LEIS, a surface is used as a target that scatters a noble gas ion beam (He
þ
,Ne
þ
,



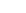






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search