Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
hence the charge associated to the adatom will not be probed by the CO adsorption,
and also because CO adsorption causes, in most cases, desorption of the adatom.
The other approach that has been proven valuable for the determination of the
PZTC of Pt electrodes is the kinetic study of N
2
O reduction [Attard and Ahmadi,
1995; Attard et al., 2004; Climent et al., 2002a]. This molecule adsorbs very
weakly on the Pt surface. As a result, the maximum rate of reduction coincides with
the maximum availability of surface sites for adsorption, and this, in turn, coincides
with the PZTC. For heterogeneous surfaces, such as Pt stepped surfaces, various
peaks in the N
2
O reduction current have been attributed to the existence of various
local PZTCs. Unfortunately, N
2
O reduction on adatom-modified surfaces is inhibited,
and therefore this method is not suitable for the PZTC determination of these surfaces.
Only the particular case of decorated stepped surfaces vicinal to Pt(111) has been
studied by these methods [Attard et al., 2004; Climent et al., 2001]. Under these con-
ditions, CO adsorption does not induce the desorption of the adatom and the catalysis
of the N
2
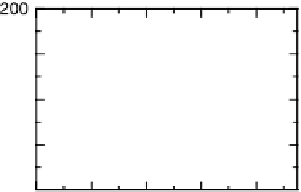
O reduction is still sizeable. Figure 7.9a, b illustrates the results of a CO
charge displacement study for the case of Pt(775) in 0.1 M HClO
4
. These plots present
the total charge curves for the bare and the step Bi-decorated surfaces, as obtained from
integration of the voltammograms, in combination with the total CO displaced charge at
0.1 and 0.2 V. For the bare stepped surface, the presence of steps causes a decrease in the
PZTC that has been explained in terms of the formation of dipoles that lower the surface
Figure 7.9 (a, b) Anodic voltammetric scan (a) and total charge density (b) of a Pt(775) elec-
trode in 0.1 M HClO
4
solution. The filled squares and circle represent the opposite of the CO
displaced charge. (c, b) Voltammograms corresponding to a Pt(332) stepped surface in 0.1 M
H
2
SO
4
solution without (c) and with (d) N
2
O. Curve A corresponds to the bare stepped surface,
while curve B corresponds to the step decorated surface by Bi deposition. Sweep rate: (a - c)
50 mV/s; (d) 10 mV/s.






















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search