Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
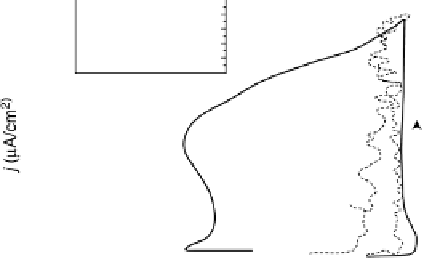
Figure 6.10 Galvanostatic scans of a Pt(110) rotating disk electrode in a CO-saturated 0.1 M
HClO
4
solution at two different current scan rates (disk rotation rate 400 rev/min). The insert
shows the potential fluctuations observed at an applied current density of 0.74 mA/cm
2
(disk
rotation rate 900 rev/min).
solutions, Pt(111) deviates from the expected values extrapolated from the observed
behavior of the stepped surfaces owing to the formation of an ordered bisulfate
layer on the Pt(111) electrode.
6.2.2 Carbon Monoxide Oxidation on Rhodium
Given the results obtained on platinum electrodes discussed in some detail in the
previous section, it is clearly of fundamental interest to study the mechanism of CO
oxidation on other transition metal electrodes, and to compare the results with plati-
num. Rhodium has been the electrode material that has been studied in greatest
detail after platinum, and results obtained with rhodium have provided some very sig-
nificant insights into some of the general issues about the CO oxidation mechanism.
From earlier work on the CO electro-oxidation on single-crystal Rh, it is known that
the reaction is much slower than on Pt, and that the stripping of a CO adlayer may take
several cyclic voltammetric scans to completely oxidize CO
ads
, from about 30 on
Rh(111) to 1 - 2 on Rh(110) [Gomez et al., 1997; Housmans and Koper, 2004].
Housmans and Koper studied this reaction in H
2
SO
4
by chronoamperometry
[Housmans and Koper, 2005a]. Figure 6.11 shows a series of transients obtained on
different stepped Rh electrodes, and it is clear that the results are very different
from those obtained with Pt. Instead of one clear oxidation peak as on Pt, CO oxidation
on single-crystal Rh exhibits two peaks: a pre-peak at short times (1 - 4 s in Fig. 6.11b)
and a main peak at longer times (5 - 50 s in Fig. 6.11a). The charge associated with the
pre-peak increases with step density, but the time of the pre-peak is not very sensitive
to the step density. On the other hand, the main peak is very structure-sensitive: it
rapidly shifts to shorter times with increasing step density, although it is virtually









































Search WWH ::

Custom Search