Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where Df
shift
(q) is the change in potential resulting from the charging process up
to the system charge Q. Accordingly, the grand canonical free energy is given by
the equation:
E
free
¼
E
DFT
þ
ð
Q
Df
shift
(q) dq
Qf
Fermi
(4
:
4)
0
The latter term arises owing to the loss or gain of Q electrons from a reservoir at poten-
tial f
Fermi
. The free energy E
free
can now be used to compare reaction energies and
activation barriers for electrocatalytic reactions as a function of the electrochemical
potential. This is demonstrated by the schematic diagram in Fig. 4.4 for the generic
reaction A
!
B, where E
free
is plotted versus potential [calculated from (4.4)] and
referenced to vacuum or the NHE. Such energies are shown as the squares and circles
for reactant and product systems, respectively, versus calculated potential in Fig. 4.4.
The encircled points correspond to the two different systems (A and B) calculated at
the same external charge. However, owing to the variation in surface - adsorbate and
surface - H
2
O interactions in the two systems, A and B at the same charge do not cor-
respond to the same surface potential. To calculate the reaction energy at a given
potential, we must instead compare the vertical energy difference between the two
best-fit curves for A and B, indicated by the length of the vertical arrow in Fig. 4.4.
Therefore, the double-reference method enables the determination of potential-
dependent aqueous phase reaction energies or activation barriers (for the latter case,
curve B is the energy of the transition state).
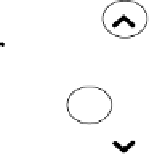
Figure 4.4 Schematic diagram of the free energy calculated from (4.4), E
free
, versus potential
ffor the generic electrocatalytic reaction A
!
B. Points indicated by squares and circles are for
specific external charges (various q) for the systems A and B, respectively. Solid and dashed
lines indicate the best-fit curves for the free energy versus potential relationship for systems
A and B, respectively.










































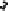















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search