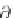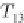Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
but the mean-plume parameters depend on turbulence statistics:
2
w
2
t
0
dσ
t
dt
+
t
)
w
p
(t)
w
p
(
t
R(t
)dt
,R t
)
=
=
=
=
2
K
,x
Ut.
w
p
As
Csanady
(
1973
) points out, the behavior of the eddy diffusivity
K
is odd when
there is more than one effluent source. If there are two sources, one upstream from
the other, then at a point where both contribute to the total mean concentration the
two effluents have different
K
values. This prompted
Taylor
(
1959
) to label the
eddy diffusivity “an illogical conception.”
4.4 Momentum flux in channel flow
In
Figure 3.1
we sketched steady turbulent flow down a channel of rectangular
cross section. We showed that the streamwise component of its mean momentum
equation is
uw
∂
∂z
ν
∂U
∂z
1
ρ
∂P
∂x
,
−
=−
(
3
.
10
)
and that the profile of the 1-3 component of its mean kinematic stress is
u
2
z
D
∗
T
13
=−
uw
+
ν∂U/∂z
=−
,
(4.30)
with 2
D
the distance between the channel walls and
u
2
the magnitude of the kine-
matic wall stress.
u
∗
is called the
friction velocity
. On smooth walls that stress is
a viscous one, but just above the diffusive sublayer it is carried by the turbulence.
For this reason
u
∗
is an important velocity scale for near-wall turbulence.
We sketch the viscous and turbulent components of this kinematic mean stress
profile in
Figure 4.3
.
The turbulent component is consistent with the existence of a
∗
Figure 4.3 A sketch of the mean kinematic stress profile
T
13
and its turbulence
and viscous components in the turbulent channel flow of
Figure 3.1
.