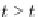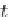Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 3.4 Schematic sketch of turbulent mixing of a contaminant, without molec-
ular diffusion (a and b) and with it (c). A key process is the deformation of the blob
by the turbulent strain field, which increases its surface area and the concentration
gradients on it, thereby greatly enhancing the molecular diffusion. Adapted from
Corrsin
(
1961
).
The first term on the far right is the rate of change of scalar gradient due to deforma-
tion by the velocity field. This mechanism can either amplify or attenuate gradients;
the gradient of a conserved scalar is not conserved. To illustrate, let the scalar iso-
surfaces be planes oriented such that their normal and the scalar gradient point in
the
x
1
-direction, say:
g
j
=
(
g
1
,
0
,
0
)
.
(3.23)