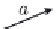Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
This produces a variable that is in effect spatially averaged over a rectangle of
streamwise length
U
1
(
2
N
+
1
)t
and width
(
2
N
+
1
)y
in the horizontal plane.
f
,sowehave
We define this as the resolved part of
f
f
r
f
s
,
r
( f
t
)
y
,
s
=
f
( f
t
)
y
.
=
+
=
−
(16.82)
Figures 6.4
and
6.5
show subfilter-scale (SFS) momentumand temperature fluxes
measured in HATS (Horizontal Array Turbulence Study). The array technique has
also been used in several subsequent field studies to give new insights into SFS
fluxes and their modeling.
16.3 Probe-induced flow distortion
Figure 16.5
shows a schematic of flow past a circular cylinder. Ahead of such an
obstacle the flow streamlines are modified by its blocking effect and the turbulence
in the flow is distorted. Since
in-situ
turbulence probes (in general we'll take
probe
to
mean the instrument plus its mounting apparatus) necessarily have some bulk, their
velocity measurements, in particular, are prone to contamination by this “probe-
induced flow distortion.”
Hunt
(
1973
) discusses two limits in this problem:
a
,where
a
is the scale
of the body and
is the integral scale of the turbulence; and
a
.
The first is
quite complicated, but the second is analytically tractable. Fortunately the second
applies to the measurement of energy-containing range turbulence structure with
flow distortion due to the probe. We'll discuss a simple analysis of it.
Figure 16.5 Flow past a circular cylinder. From
Hunt
(
1973
).