Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
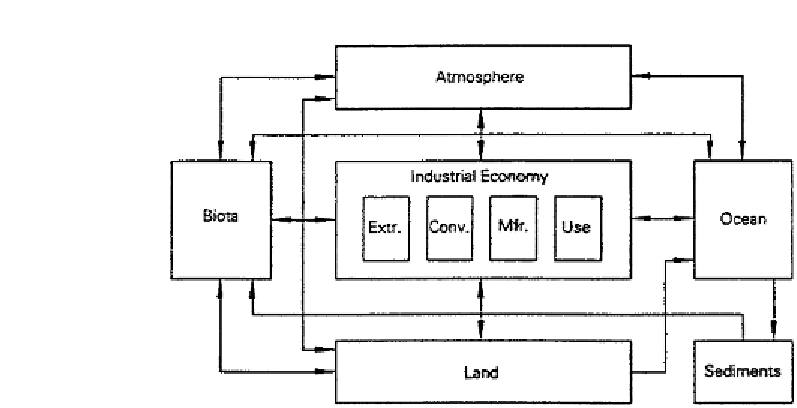
FIGURE 1
Flow of materials and energy through an industrial ecosystem from the perspective
of the product life cycle. (Hardin Tibbs)
“Scenery,'Environmental Conditioning' ” refer to how ordinary consumers
use the materials and energy of the natural world.“Agriculture & Forestry”
and “Mining & Drilling” are also broken out, as are the forms of natural
resources that people use and the ways they utilize them.All these functions
and resources are bound up in the materials and energy flows of a generic
industrial ecosystem.This diagram provides an in-depth sense of industrial
ecology, for it depicts more of the social and environmental context in
which business operates and goods are manufactured and used.
4
Wastes are generated at every stage of this systems flow. The process by
which resources are extracted from the natural world generates wastes, as
does the manufacturing process. The same is true of distribution and con-
sumption, as the diagrams make clear. These wastes may take the form of
air or water pollution or solid waste. These emissions can cause significant
disruptions to natural ecosystems. Mitigation of these impacts requires
management at every stage of the production and consumption cycle, not
just the manufacturing stage.
In my view, it is absolutely essential that historians start putting business
into the larger eco-industrial context embodied in these concepts and dia-
grams. Business historians need to broaden their analysis of the evolution of
business institutions and management strategies to incorporate analysis of