Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 7.9.
Problematic preprocessed examples from the Swedish Post database. In some ex-
amples the digit segmentation is difficult, while in others the recognition of isolated digits is
hard.
Output
Input
Layer 0 (32x16x1)
Layer 1 (16x8x4)
Layer 2 (8x4x16)
Layer 3 (4x2x32)
Fig. 7.10.
Network architecture for meter value recognition. It is a feed-forward version of
the Neural Abstraction Pyramid with specific excitation and unspecific inhibition in the inner
layers. The activities of the trained network for a test example are shown. The output feature
cells signal the classes of the two digits of interest in a 2
×
(1-out-of-10) code ('
3
' and '
5
' for
a meter value
3.50
).
One could now try to segment the digit block into single digits, recognize them,
and combine the digit classifier outputs to a meter value. This approach would re-
quire reliable digit segmentation and a reliable digit classification system. Both re-
quirements are not easy to meet. It is fairly hard to segment the digits, and it is also
difficult to read isolated digits reliably, as is evident from Figure 7.9 which shows
some problematic preprocessed meter values.
For these reasons, a block classifier was developed that recognizes the two digits
of interest simultaneously within the context of the neighboring digits. Unlike a digit
classifier that can only use the a-priori distribution of single digits, this classifier is
able to take advantage of the non-uniform meter value distribution, summarized in
Table 7.1.
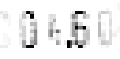



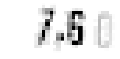
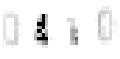

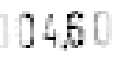
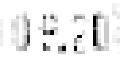
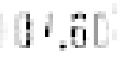


Search WWH ::

Custom Search