Database Reference
In-Depth Information
(iii) summarize and cluster events that exhibit similar spatio-temporal
properties among multiple variables.
Applications of event detection techniques involve monitoring changes
occurring over either land, ocean, atmosphere or biosphere. For instance,
vegetation time series (e.g., the Enhanced Vegetation Index from the
MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Earth observing Terra and Aqua
satellites) can be used to detect a variety of events, such as deforesta-
tion, floods, fires, etc., that result in a perceptible change in vegetation
[2, 50].
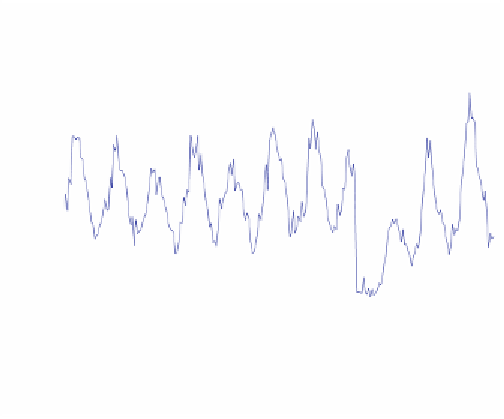
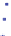
Figure 15.2
provides an example of a vegetation time series at
a particular location which got burned in the year 2008, showing a sig-
nificant drop in the vegetation value in that year. Furthermore, land
cover change detection using vegetation time series can be further en-
hanced by utilizing information about the thermal anomaly time series
(available through MODIS), for characterizing fire events which register
a thermal anomaly observation, from other land cover events such as
deforestation, droughts etc. As another example, sea surface height can
be used for detecting ocean eddies which are swirls of ocean currents
playing a crucial role in transporting water, salt, heat, and nutrients in
the ocean, as well as driving the ocean's dynamics [23].
9000
8000
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
Time
Figure 15.2.
An example vegetation time series of a fire event at a particular location.
The Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) shows a characteristic drop in the year 2008
during the event of the fire.