Database Reference
In-Depth Information
41
53
52
40.5
51
40
50
49
39.5
48
47
39
90
95
100
105
110
40
60
80
100
120
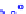
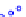
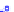
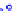
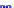
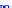
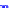
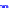
x
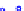
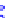
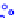
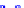
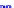
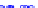
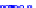
x
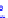
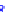
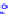
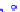
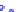
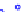
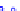
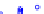
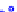
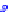
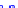
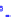
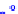
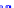
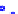
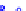
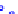
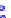
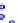
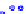
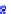
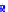
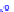
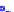
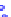
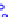
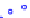
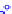
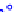
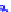
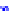
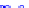
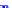
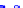
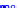
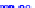
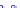
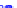
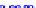
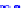
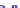
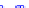
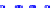
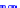
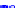
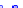
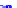
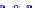
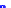
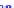
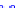
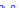
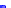
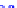
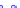
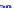
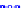
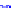
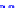
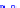
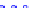
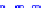
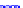
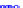
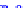
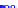
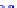
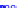
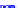
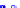
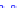
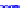
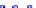
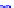
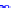
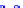
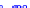
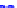
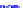
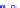
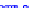
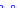
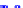
(a) Joint Gaussian
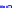
(b) Conditional Gaussian
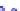
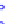
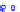
Figure 10.8.
A joint Gaussian distribution of two random variables is shown in fig-
ure (a). In (b), we show the result of the distribution over
x
after conditioning on the
value of
y
.
the original variance term for the observed variable as well as the shift of
the observation from the expected value. Notice that if our observation
matches the expected value,
μ
y
, or the covariance between
x
and
y
is
small, then the correction term is small and thus observing
y
provides
little information about
x
. Similarly, the covariance is corrected accord-
ing to the covariance and variance term of the observed variable. Notice
here that the correction term is subtracted from the original variance.
Since the covariance matrix is positive semi-definite, conditioning on an
observed value is guaranteed to decrease variance and therefore reduce
our uncertainty about the variable of interest.
Figure 3.2.1 shows an example of two variables that are jointly nor-
mally distributed. There is strong correlation between the two variables
bution over
x
changes by shifting (correction to the mean) and scaling
(reduction in variance).
3.2.2 Filtering.
There are three types of inference we will be
interested in computing with the KFM: prediction, filtering, and smooth-
ing.
Figure 3.1
shows each of the different procedures, highlighting the
variables and connections which are used in each. We will first discuss
the filtering problem, updating our parameters of interest upon the ar-
rival of new observations, which subsumes the task of prediction. Then,
we will introduce smoothing, estimating parameters given past
and fu-
ture
observations, which is an oine task that typically provides more
accurate estimates with reduced uncertainty.
The objective of filtering is to update our estimates by incorporating
the most recent observation. For the KFM, the posterior takes the form