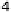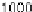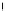Database Reference
In-Depth Information
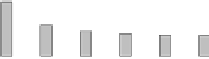
(a) Testbed (2 hours).
(b) Tunnel (23 hours).
Figure 7.7.
Average duty cycle [79]. (Note the difference in the
y
-axis scale.)
data), representative of scenarios with different connectivity. Based on
a 47-day, 40-node dataset gathered in this deployment, the study shows
that DBP suppresses 99% of the message reports (w.r.t. the baseline,
where all nodes send data every 30 sec).
This study examined how data delivery to the application, network
lifetime, and routing costs are affected by DBP. To study the impact
on lifetime, the study measured the duty cycle of the radio, which is
the most power-consuming component.
Figure 7.7
clearly shows that
DBP enables significant savings at any sleep interval, while the best
sleep interval without DBP is 1500 ms . When using DBP, longer sleep
intervals can be used to increase lifetime without affecting data delivery.
Figure 7.7(a)
shows that in the testbed, with a sleep interval of 1500 ms
the WSN running DBP lasts twice as long as with no DBP (with the
same MAC settings). Using the best sleep interval in both cases (i.e.,
1500 and 3000 ms, respectively) yields a three-fold lifetime improve-
ment
8
.
A natural question arises at this point: if DBP suppresses over 99%
of the messages, why does the network lifetime increase “only” three-
fold? This is due to the costs of the network stack, in particular the
idle listening and average transmission times of the MAC protocol, and
to the overhead of the routing protocol to build and maintain the data
collection tree.
To isolate the inherent costs (e.g., tree maintenance) of CTP, experi-
ments were ran with no application trac.
Figure 7.7
shows the corre-
sponding duty cycle (as
Only CTP
). We observe that the DBP cost is
8
The energy savings in the tunnel (see
Figure 7.7(b)
)
are less remarkable, although still
significant, because the network diameter in the tunnel is much smaller w.r.t. the testbed
(due to the waveguide effect [66] many direct, 1-hop links to the sink exist, leaving less room
for improvement).