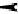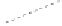Database Reference
In-Depth Information
x 10
−4
Sine (period 50) − Power profile
Power
∝
1/w
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
Window size (w = 10..400)
Figure 5.5.
Powerprofileofsinewave
x
t
=sin(2
πt/
50) +
t
, with Gaussian noise
t
∼N
(5
,
0
.
5).
X
(4,0)
time
delayed
coordinates
proj.
proj.
proj.
proj.
project onto
local patterns
X
(4,1)
delayed
coordinates
proj.
proj.
project onto
local patterns
X
(4,2)
delayed
coordinates
proj.
project onto
local patterns
patterns for wind. 4
+
x
v
(4,0)
x
1
x
v
(4,0)
x
+
2
v
(4,1)
v0
(4,1)
1
1
(4,1)
v
"equivalent" pattern for window 8
2
Figure 5.6.
Multi-scale pattern discovery (hierarchical,
w
0
=4,
W
=2,
k
=2).
8.1.1 Power Profile.
Next, let us assume we have optimal
local patterns for a number of different window sizes. Which of these
windows is the best to describe the main trends? Intuitively, the key
idea is that if there is a trend that repeats with a period of
T
,thendif-
ferent subsequences in the time-delay coordinate space should be highly
correlated when
w
T
. Although the trends can be arbitrary, we il-
lustrate the intuition with a sine wave, in
Figure 5.5
. The plot shows
the squared approximation error per window element, using
k
=1pat-
≈