Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
the chromosome aberrations assay with
A. cepa
, can be used as a tool for quantifying and
monitoring genetic alterations in soils radioactively contaminated. Moreover, the
chromosome aberration assay in onion was the first of nine plant systems accepted in the
Genotoxic Program of the Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) and is widely used
for monitoring residual water. Such sensitivity is attributed by Ma et al
.
(1995), to the large
size of the chromosomes and because they are mostly metacentric. On the other hand,
bioassays based on chromosome aberrations, in certain cases, tend to be replaced by less
time-consuming techniques, such as the micronucleus assay (MN), which can be performed
with mitotic cells in roots (of
V. faba
or
A. cepa
) or meiotic cells, in tetrads of
Tradescantia
(Misik et al., 2011).
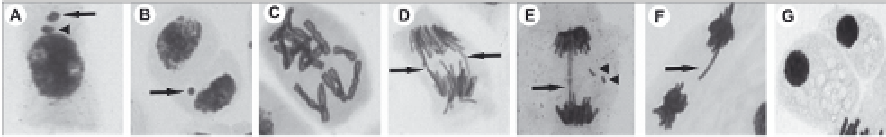
Fig. 6. Alterations observed in
A. cepa
meristematic cells. (A) nuclear bud (arrow head) and
micronucleus (arrow); (B) micronucleus (arrow); (C) C-metaphase; (D) anaphase with
chromossomal bridge (arrows); (E) telophase with cromossomal bridge (arrow) and
chromossomal break (arrows head); (F) telophase with cromossomal delay (arrow); (G) cell
death. (Photos: Cintya Aparecida Christofoletti)
The micronucleus test in
Tradescantia
(Trad-MCN) (figure 7) is a sensitive mutagenicity test,
of short exposure and simple evaluation, applicable in the species
T. pallida
and in the clones
BNL 4430 and KU 20 (Misik et al., 2011). Besides the Trad-MCN, it is possible to evaluate
mutations in somatic cells of the staminal hair (Trad-SHM) in young inflorescences of the
hybrid clone BNL 4430 (Brookhaven National Laboratory). However, currently, the clone
KU 20 (Kyoto University) is more applicable to this technique due to the higher number of
inflorescences per cycle. The mutation results in the expression of the recessive allele, which
implies in the phenotype of pink colouration. The high rate of pink cells, as well as the loss
of reproductive capacity are indicative of mutagenicity (Ma et al., 1996).
Fig. 7. Micronucleus in polen cells of
Tradescantia
(arrow in B). (Photos: Janaína Pedro-Escher)
4.3 Molecular biomarkers
The use of molecular biomarkers in the environment monitoring represents a significative
tool for the evaluation of the contamination in different organisms. Despite morphological
markers provide good qualitative evidence of damages caused by certain pollutants, it is
known that biochemical alterations resulted from the toxic action of a contaminant are early
evidence of negative effects of the exposure, since they precede the onset of visible damages.