Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
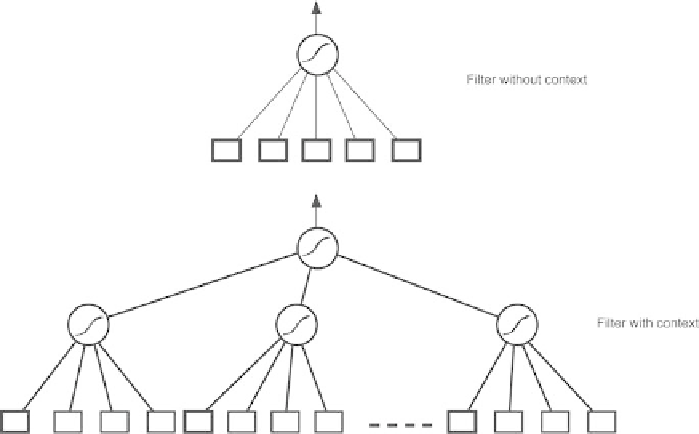
Fig. 1.39.
A filter without context is a linear classifier whose inputs are the features
that encode each word of the specific vocabulary (
rectangles in thick lines
); in a
filter with context, the inputs are the features that encode the words of the specific
vocabulary (
boxes in thick lines
), and, in addition, the features that encode the
context words (
boxes in thin lines
)
Filters with Context
The context must have an influence of the feature that encodes each word
of the specific vocabulary. Therefore, the filter represents each word of the
specific vocabulary by a neuron with sigmoid activation function, whose inputs
are
•
the feature that encodes the word of interest,
•
the features that encode the context words of that word.
The outputs of those neurons are separated linearly by a neuron with sigmoid
activation function. Figure 1.39 shows a filter with context and a filter without
context.
The introduction of context words as inputs increases the number of pa-
rameters of the classifier. Typically, for a topic with 25 words of specific vo-
cabulary, and 3 context words per word of the specific vocabulary, the filter
has 151 parameters. Since some topics are described by a small number of
relevant texts, the use of a regularization method is mandatory. The weight
decay method (described in Chap. 2) proved useful in the present application;
its effect and implementation are explained in Chap. 2, in the section devoted
to regularization techniques.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search