Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
If
X
ij
and
Y
ij
are the distances between points
i
and
j
, computed in the
original space and in the reduced space respectively, one has:
original space:
X
ij
=
k
=1
(
x
ik
−
•
x
jk
)
2
,
reduced space:
Y
ij
=
n
•
k
=1
(
y
ik
−y
jk
)
2
.
The transformation of components generates a distortion of the variety. By
retaining the same metrics (euclidean distance), a measurement of distortion
may be given by comparing distances
X
ij
with distances
Y
ij
:
p
p
(
X
ij
−Y
ij
)
2
.
i
=1
j
=
i
+1
A parallel may be drawn with PCA, which defines linear projection by min-
imizing the objective function:
i,j
X
2
ij
−
i,j
Y
2
. That function expresses
ij
the difference between the average of distances
X
2
ij
computed in the original
space and the average of distances
Y
2
ij
computed in the reduced space. By
contrast, the cost function used for CCA tends to preserve differences in dis-
tances
X
ij
−
Y
ij
, and is therefore used to represent nonlinear varieties with
minimum distortion.
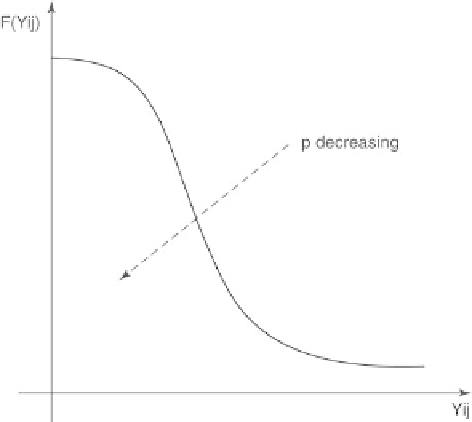
In order to be able to unfold the varieties, a weighting term
F
(
Y
ij
,ρ
),
which a decreasing positive function of distance
Y
ij
, may be introduced in the
cost function (Fig. 3.6).
The term
F
(
Y
ij
) favors short distances in projection space. Parameter
ρ
plays the same role as the radius parameter defined in Kohonen maps: in
Fig. 3.6.
Distance weighting function
Search WWH ::

Custom Search