Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
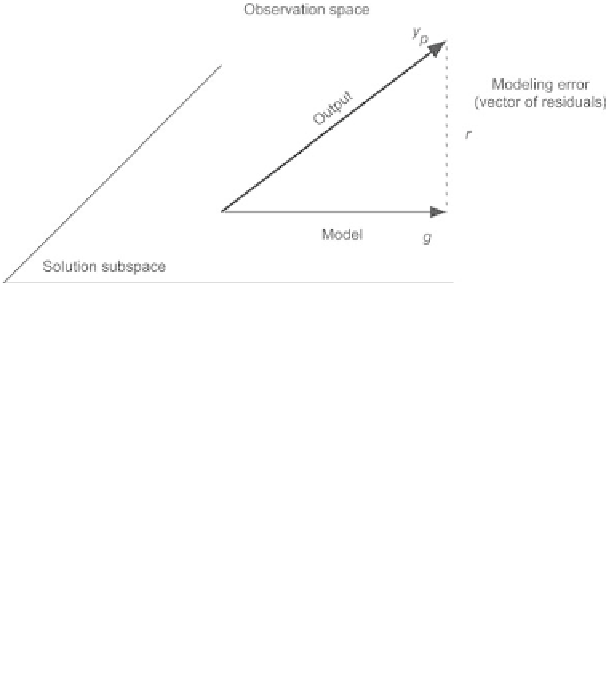
Fig. 2.5.
Geometrical interpretation of the least squares method
z
3
z
1
y
p
ξ
1
g
z
2
ξ
2
Fig. 2.6.
Geometrical interpretation of the least squares method: a 3-dimensional
example
2.5.1.2 Adaptive (On-Line) Training of Models that are Linear
with Respect to Their Parameters: The Least Mean
Squares Algorithm
In adaptive training, the parameters of the model are updated as a function
of each example taken separately; this is especially useful for adaptive filter-
ing or adaptive control, where the model must be adapted to the evolution
of the process to be modeled. The
recursive least squares
algorithms find
adaptively the least squares solution, for a model that is linear with respect
to its parameters [Ljung 1987; Haykin 1994].
Among recursive least squares algorithms, the least mean squares (LMS)
algorithm (widely used in linear adaptive filtering), also called Widrow-Hoff
algorithm [Widrow 1960]) is also used for training neural networks adaptively.
It updates the parameters as a function of the gradient of the partial cost




















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search