Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
1000
100
10
10
100
1000*(R - Rmin)/(R + 1)
1000
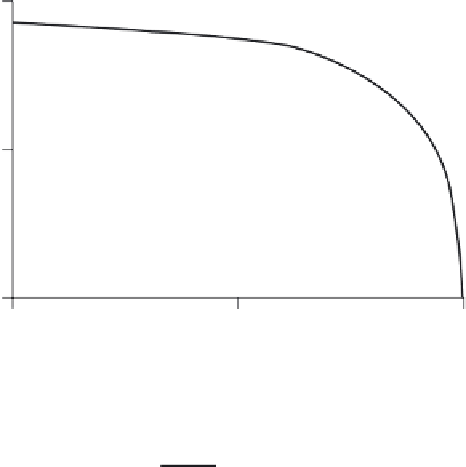
Figure 11.10
Gilliland correlation.
α
i
z
i
α
i
− θ
=
1
−
q
(11.9)
i
Here
α
i
is the relative volatility of component
i
,
z
i
is the mole fraction in the feed of
component
i
,
q
is the thermal state of the feed, using the McCabe-Thiele definition,
and
θ
is a root of the equation. To calculate the minimum reflux ratio, the value of
θ
,
which lies between the light and heavy keys, is substituted into the equation
α
i
x
i
α
i
− θ
R
min
+
1
=
(11.10)
i
where
x
i
refers to the mole fraction of component
i
in the distillate.
The minimum number of stages is calculated using Winn's (1958) equation, an
improvement on Fenske's (1932) equation, where the usual definition of relative volatil-
ity is replaced by
K
i
= β
i
(K
R
)
θ
i
(11.11)
and the parameters
β
i
and
θ
i
are determined from the equilibrium data for each com-
ponent. Winn's equation is
ln
(x
D
/x
B
)
LK
(x
B
/x
D
)
θ
LK
HK
N
min
=
(11.12)
ln
β
LK
The procedure for estimating the distribution of nonkey components is as follows.
Assuming that the equation
d
i
b
i
=
d
r
b
r
α
i,r
(11.13)