Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
For the structural discussion of this report, a CCDC search [143] for com-
pounds containing X
2
or XY molecules with intermolecular B
X(B=N,O,
P, S, As, Se; X = Cl, Br, I; Y = Cl, Br, I)
1
distances less than the sum of their
van der Waals radii was performed. Results which did not include atomic
coordinates, or those reporting crystallographically disordered or otherwise
structurally suspect results, were ignored. Ionic salts were included only if
they also contained halogen bonded adducts, or served as interesting data
points along the complex-ionic salt continuum. Metric data for the resulting
210 complexes are reported in Tables 1-3 for nitrogen and oxygen, phospho-
rus and sulfur, and arsenic and selenium, respectively.
Depending on a complex balance of the strength of the electron donor-
halogen interaction, packing requirements resulting from the size and shape
of the electron donor B, the presence, strength, and directionality of other
attractive interactions, and the ability, particularly of iodine, but also to
more limited extents of bromine and chlorine, to catenate through halogen-
halogen donor-acceptor interactions, several different structural modes are
observed.
Electron donors which interact at only one end of the X
2
or XY molecule
form simple adducts (Fig. 1, mode
A
), often referred to as a “spoke”
structure. The diiodine complex of tris(diethylamino)phosphine selenide
(PAQKIB) [135] shown in Fig. 2a is an excellent example of this mode, as the
Se
···
I distance at one end of the I
2
molecule is 2.715
A
, while at the other end
there are no close contacts with any other atom.
···
Fig. 1
Dihalogen interaction modes
X interactions occur at either end of the dihalogen, the electron
acceptor molecule serves as a bridge (Fig. 1, mode
B
). This interaction more
typically occurs with weaker electron donors, as a strong donor polarizes the
dihalogen to the extent that the Lewis acidity of the second halogen atom is
When B
···
1
Despite a recent computational article suggesting that organofluorine compounds could partici-
pate in halogen bonding [190], to date no F
2
complexes have been observed in the solid state.


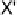
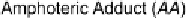
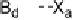

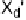
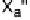
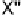

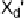
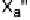
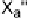
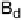

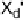



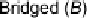















Search WWH ::

Custom Search