Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
6-311++G(d,p) and correcting for BSSEs using the counterpoise method, the
authors examined the effect of cooperativity on the halogen bond strength.
That is, after performing a full geometry optimization of the 1 : 1 complex,
they added a second ClF molecule to the system. Geometry optimization of
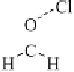
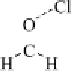
thenewcomplexgavestructure
2
, where the fluorine on the first ClF acts
as an electron donor to the second ClF. Interestingly, the calculated O
Cl
bond length decreases as the second halogen bond is formed. Extension of
the ClF
···
ClF chain out to six interhalogen units (
3
,where
n
=5) resulted
in further shortening of the O
···
Cl bond, and a corresponding increase in
the halogen bond energy. The authors conclude that cooperativity in halogen
bonding is similar to the effect observed in hydrogen bonded systems.
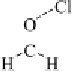
···
Structure 1
3.3
Nitrogen Electron Donors
The pyridine-I
2
system has received considerable attention over the years.
While the single crystal diffraction data for this complex have not been
reported, closely related structures are known, including 4-methylpyridine-
I
2
[42] and pyridine-ICl [163]. Studies of pyridine-I
2
in solution give a dipole
moment of 4.5-6.3 D and a binding energy of 7.4-8.6 kcal
/
mol, depending on
the solvent [164-168]. Bopp and coworkers have studied the systems using
ab initio methods (MP2) and compared several basis sets, including both all-
electron and effective core potential basis sets [169]. In addition to examining
the geometry and binding energies of the system, the vibrational frequencies
were also computed and compared to experiment [170]. While ultimately un-
satisfied with the level of accuracy obtainable with the available computers,
the group was able to show that inclusion of electron correlation is important.
The smaller effective core potential basis sets were not particularly accurate,
but the authors suggest they might be used if their shortcomings were well
described and could be taken into account.
Karpfen published a study of trends in halogen bonding between a series
of amines and halogens and interhalogens [171]. Iodine-containing electron
acceptors were not included. This study involved the use of RHF, MP2, and
various DFT methods using extended, polarized basis sets and made exten-
sive use of pulsed-nozzle, FT-microwave spectroscopic data (similar to that
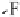
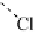
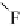
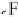
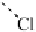
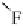
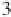
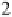







Search WWH ::

Custom Search