Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
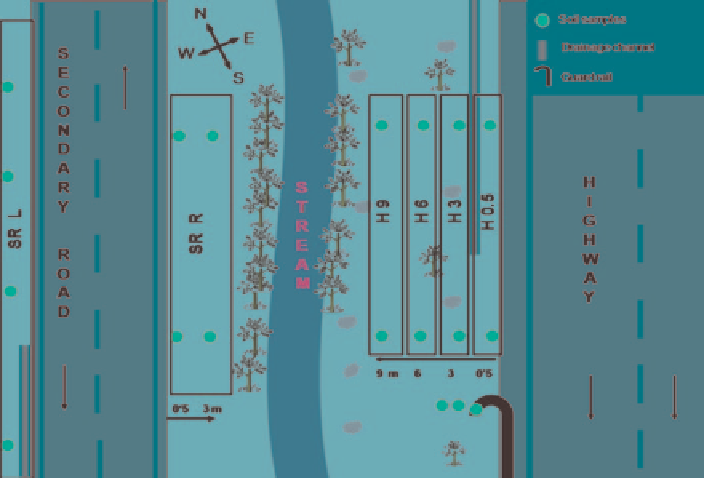
Fig. 2
Experimental design of the sampling area
Roadside soil samples were collected at different sampling points along both
roads during May of 2007. Sampling in the highway was carried out at a distance
of 0.5, 3, 6 and 9 m from the highway (H 0.5, H 3, H 6 and H 9 sampling areas)
(Fig.
2
). In the secondary road samples were collected at both roadsides (SR L and
SR R sampling areas) but the sampling was only completed at 0.5 m in the west
roadside and at 3 m in the east roadside because of the existence of a road cut and
a stream that avoided sampling at a further distance.
Soil samples under the guard rail were also collected (GR 1-GR 3). Control soils
were sampled 700 m away from both traffic roads in the north-west direction. Soil
samples were collected from the upper 0-20 cm of soil, subsequently air dried in a
fume hood during 24 h and then milled and sieved to <2 mm.
The analytical determination of heavy metals in soil samples were carried out
following the US Environmental Pollution Agency EPA 3051A method which
describes the “microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludge, soils, and
oils”
[11]
. The method consists in the digestion of 0.5 g of soil sample with a
mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrochloric acid (9:3) in a
fluorocarbon polymer (PTFE) microwave vessel at the temperature of 170°C
(±10°C) during 4.5 min (Table
1
). A first ramp of 1,000 W was applied during 7 min
to reach 170°C as established in the method, and then it was maintained by means
of a second ramp of 800 W during 4.5 min. The extracts were filtered through a
0.45 mm PVDF filter in a 50 mL polypropylene tube. The residual soil and the vessels
were washed several times with Milli-Q water and the extracts were mixed.