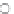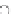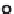Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
paired with road dust samples with higher precious metal values. The decrease in
the Au, Pt, Pd and Rh concentrations in the gullies compared with the road dust is
most marked at sites where the precious metal concentration in the road dust is
highest. For example at site F, collected in summer 2006, the concentrations in road
dust are reduced in gully waste from 25 to 15 ppb Au, from 50 to 40 ppb Pt, from
165 to 55 ppb Pd and from 20 to 10 ppb Rh.
The Pt/Pd ratio for all the samples is approximately 1.0 but varies from 0.2 to 8.8.
For the paired summer 2006 road dust and gully sediment collected during dry con-
ditions Pt/Pd ratios are generally similar (Fig.
4a
, Table
1
). In contrast the Pt/Pd
ratios for the paired winter 2006 samples collected in rainy conditions show higher
Pt/Pd ratios for the gullies than for the road dust. Pt/Rh ratios vary from 2 to 6 with
an average of 3.7 and do not show any systematic variation between winter and sum-
mer samples or between road dust and gully samples (Fig.
4b
, Table
1
). Similarly
there is no systematic difference between Pt/Au ratios in the summer or winter.
100
Pt
10
1
1
10
100
1000
Pd
100
10
Pt
Road dust Winter 05
Road dust Summer 06
Road dust Winter 06
Gully Summer 06
Gully Winter 06
1
1
10
100
Rh
Fig. 4
Graphs of (
a
) Pt versus Pd and (
b
) Pt versus Rh.
Dashed
and
dotted circles
show separation
of data sets