Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0,90
1,2
mov. aver. TSP
mov. aver. Pb/Ti
1,0
0,75
0,60
0,8
0,6
0,45
0,30
0,4
0,2
0,15
0,00
0,0
week
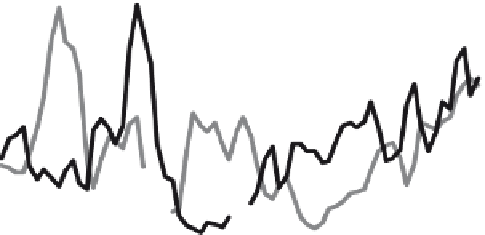
Fig. 3
Moving average of TSP mass concentration and the ration of Pb and Ti concentration
between mid 2005 and end of 2006 at site 4 (SE Beijing)
Besides Pb, also Zn indicates the ubiquitous anthropogenic aerosol pollution in
urban systems, since it is released during various combustion and abrasion processes.
For the PM
2.5
fraction, Pb and Zn mass concentrations calculated as µg/m
3
stay
below 0.5 mg/m
3
, but are considerable higher than what is found in New York and
Baltimore
[18, 24-26]
. Up to more than twofold of Pb and Zn concentrations (µg/m
3
)
in PM
2.5
were observed in the TSP fraction. However, Pb and Zn concentrations
calculated as µg/g were lower in TSP than in PM
2.5
.
Thus, the particle size fraction above 2.5 mm considerable contributes to the
overall particle mass, but dilutes the metal concentrations within the particle mass.
Nevertheless, within the TSP fraction, Pb and Zn concentrations still reach on average
1,000 and 2,500 mg/g, respectively. Lead and Zn concentrations in PM
2.5
exceed up
to more as twice as much those in TSP. It is noteworthy to highlight the situation at
site three located just near to the central Tienamen Square. Here the Pb and Zn mass
concentrations expressed in µg/m
3
are less than at the sites northwest and southeast,
but highest if expressed in µg/g. Those high concentrations might contribute to the
health harming potential of aerosols although no standards are set for harmful metal
concentrations in µg/g, yet (Fig.
4
).
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that PM
2.5
concentrations are varying in the Beijing area.
Lowest aerosol concentrations occurred during summer, whereas spring show high
aerosol concentrations predominantly caused by geogenic particles, and winter is a