Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 5.5 Products of test
shop with their prices
Product ID
Price
1
12.00
2
10.00
3
4.00
4
140.00
5
15.00
6
4.50
0.5
0.25
0.33
0.33
0.33
0.33
0.17
0.25
0.33
0.25
0.33
1.0
0.33
0.33
0.17
0.5
s
G
s
s
3
s
s
5
s
6
s
4
s
A
1
2
0.33
0.33
0.25
0.33
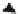
Fig. 5.7 Transition probabilities for the test shop
•1
!
5
*
!
4
!
3
!
4
*
!
5
!
4
!
2
*
!
4
!
2
!
5
!
6
*
•6
!
1
*
!
4
•6
!
4
*
•5
!
2
!
1
We further suppose that during the sessions no recommendations have been
displayed. Then we can easily calculate the unconditional transition probabilities.
They are shown in Fig.
5.7
When we look at the graph
Γ
(
P
) induced by these
transition probabilities
P
, we see that it is strongly connected and thus
P
is irreducible.
We next establish 3 different functions to derive the conditional probabilities
from the unconditional ones:
(a)
p
ss
a
¼
p
p
ss
a
(b)
p
ss
a
¼ p
ss
a
(c)
p
ss
a
¼ p
ss
a
=
2
Due to Assumption 5.2 all probabilities
p
ss
0
are completely defined.
For this simple example, we now run the simulation using the DP-Version. First
we verify the estimation of the transition probabilities proposed in Sect.
5.2.3
.