Graphics Programs Reference
In-Depth Information
Filled regions
allow you to choose from a variety of hatch patterns to fill the region. These
are commonly used in details to illustrate materials like rigid insulation, concrete, or plywood.
Masking regions
, on the other hand, do not include a fill pattern. Masking regions are typically
used to “hide” or
mask
certain content from a view that you don't want shown or printed. As an
example, there might be a particularly detailed way in which two walls join and their materials
overlap. In some cases, it doesn't make sense to model that condition, and it makes more sense
to use detail lines to describe the condition. Here you would need to mask a portion of the view
so you can essentially draw over it with new content.
When selecting the Region tool, you will be taken directly into Sketch mode, and you'll have
a series of tools similar to those for drawing detail lines. The Draw panel allows you to create
any number of shapes with all the associated tools to move, copy, or offset the linework.
When creating either kind of region, it's important to note that you cannot complete Sketch
mode unless the boundaries you draw are in closed loops. You can create as many closed-loop
boundaries as you want as long as they do not overlap and are all formed with closed loops
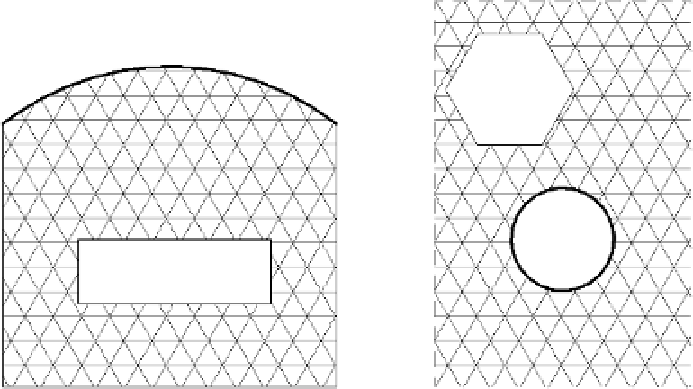
(Figure 16.6). Notice in the figure that, in addition to the use of multiple closed loops, you can
use any combination of line styles to draw the boundary of a region.
Figure 16.6
Multiple shapes within
a single filled region
Another consideration for using regions is the linework that borders a region. When starting
the Region tool, you'll be able to choose the line style you want to use for the border of the
region from the Line Style drop-down (similar to working with detail lines). You can change
line styles for any of the segments of the region and even make them all different if needed.
One especially useful segment line style is <Invisible Lines>. When drawn in Sketch mode,
these appear as gray lines, but once the sketch is completed, they become invisible lines. When
used with a masking region, this line style can create a completely invisible box that allows
you to hide elements that are unwanted in a particular view. Figure 16.7 shows the same
masking region in two instances, one selected and the other not selected. You can see how
the masking region seems to disappear, covering the filled region. Use caution if you decide
to use masking regions with invisible boundary lines because you will not be aware of their
existence unless you hover the mouse pointer over them. In the example shown in Figure 16.7,
the end result can also be achieved by drawing two additional invisible lines in the filled region.