Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
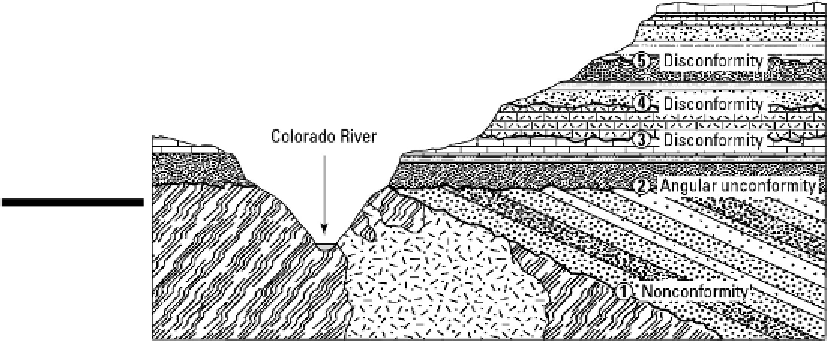
The Grand Canyon in Arizona is an excellent example of stratigraphy exhibiting these
different types of unconformities. Figure 16-3 is a sketch of the Grand Canyon strati-
graphy with the different types of unconformities labeled.
Figure 16-3:
The
Grand Canyon ex-
hibits a noncon-
formity (1), an an-
gular unconformity
(2), and multiple
disconformities (3,
4, and 5).
Show Me the Numbers: Methods of Abso-
lute Dating
The principles of stratigraphy and relative dating provide a sequence of events for geo-
logic history, but they cannot tell you how old something is in years. To answer that
question, scientists must use absolute dating techniques.
An
absolute date
is the numerical age of something. Again, consider describing the age of
your family members. This time, provide absolute dates instead of relative dates. You
may say that your sister is 15 years old and your brother is 27 years old. These are their
absolute, numerical ages — nothing relative about it!
Measuring radioactive decay
The most common method used to determine the numeric age of rocks is called
ra-
diometric dating.
This method measures the
decay,
or atomic changes, in certain atoms.
To help you understand radioactive decay, I need to review briefly some information
about atoms from Chapter 5.