Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
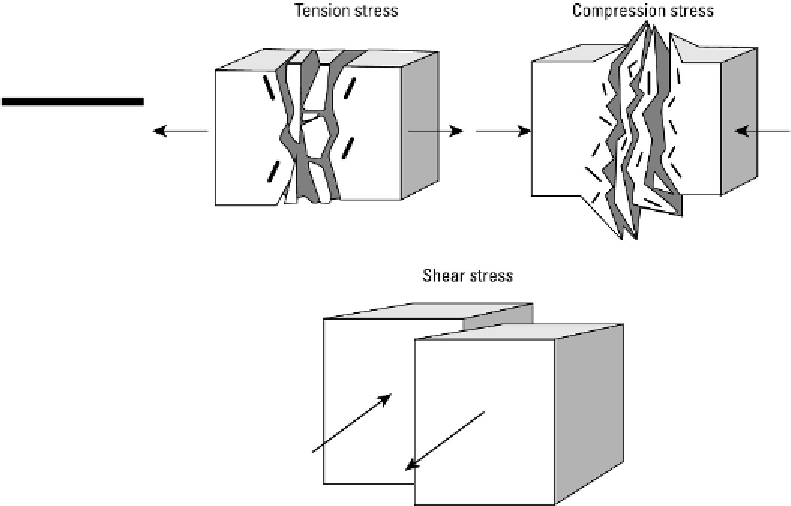
Compression
is what occurs at convergent boundaries where two plates move toward
one another and compress or crush the rocks in between them. The opposite occurs at
divergent boundaries, where the plates are moving apart and create
tensionstress
by
stretching the rocks between them. And at transform boundaries, as the plates move in
opposite directions alongside (parallel to) one another, the rocks between them experi-
ence
shearing stress
as they break apart and move with one plate or the other. Each type
of stress is illustrated in Figure 9-9.
Figure 9-9:
Three
types of rock
stress.
When an object responds to stress by simply breaking, it experiences
brittle failure
or
brittle deformation.
This response may happen with rocks if the stress is applied sud-
denly, especially if the rocks are near earth's surface and relatively cool.
Deeper in the earth's crust, rocks are exposed to higher heat and slowly building pres-
sure. These rocks are more likely to respond to stress with
ductile
or
plastic deformation:
a change in their shape without breaking or fracturing.
Compressing rocks into folds
At convergent plate boundaries, rock layers are often compressed into folds. Folds in
rocks may be small enough to see in a rock you hold in your hand or large enough to