Travel Reference
In-Depth Information
rural tourism development in Lithuania, parti-
cularly the way that local and regional tourism
planning is vertically integrated with national
development objectives, and the way that finan-
cial incentivization is used to coordinate rural
tourism development in the three case studies
presented in this chapter.
involving elderly people, reducing depopulation
in rural regions and minimizing the unemploy-
ment rate and antisocial phenomena. Rural
leisure and tourism activities are recognized
as encouraging understanding of Lithuanian
culture and traditions, encouraging mobility
and impacting positively on human health.
However, there has been conflict between pro-
tection of the natural territories and the private
interests of land owners.
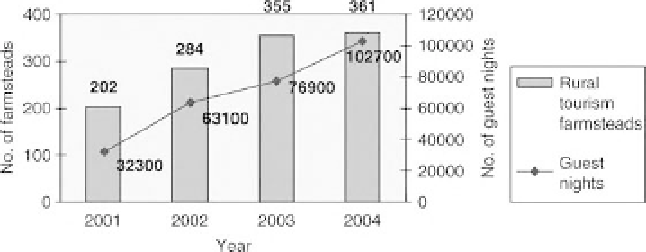
Rural tourism is growing rapidly in Lithuania
with the number of visitors increasing from 18%
to 49% between 1999 and 2004. The number
of officially registered rural tourism service pro-
viders has grown fourfold from 89 registered
providers in 2000 to 361 in 2004 and growth in
demand for tourism is constrained by the rate of
growth in supply, especially of accommodation
(see Fig. 15.1). However, despite raised aware-
ness of sustainability issues in Lithuania at a policy
level, sustainability terms are not used to market
Lithuania at a national, regional, local or indi-
vidual tourism business level, and terms such as
'undamaged nature', 'natural spaces', 'ecological
farm', 'natural vegetables and food' prevail.
However, this is probably more a reflection of
the market than of attitudes towards sustainable
rural tourism development in Lithuania.
Rural Tourism Development
in Lithuania
The 'flagships' for sustainable rural tourism
development in Lithuania are its five national
and 30 regional parks and these territories were
the first to be involved in the implementation of
Agenda 21 in Lithuania. Lithuania has a mild
climate and a diverse and beautiful landscape
with enormous potential for a wide variety of
recreational activities. It has a rich history and
cultural heritage through the broad ethnic mix
of its population that creates favourable precon-
ditions for tourism development and can lead to
enhanced employment opportunities and income
generation. Tourism has been recognized in
the post-Communist transition of Lithuania to a
market economy and the economic restructur-
ing therein as a vehicle for balancing the
economic, social and environmental agendas,
especially in rural areas. Tourism development
in rural areas enables not only social and
economic development through exploitation of
Lithuania's rich natural and cultural resources,
but also ensures their ongoing conservation
which can be under threat at times of economic
downturn. Rural tourism development is seen as
The Lithuanian Policy Framework
for Sustainable Rural Tourism
Development
As widely documented, the concept of sustain-
ability and Agenda 21 dates back to 1992 and
Fig. 15.1.
Lithuania: rapid growth of rural tourism, 2001-2004. Source: compiled by A. Armaitien
,
h
2005, using statistics from the Lithuanian State Tourism Department website at