Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
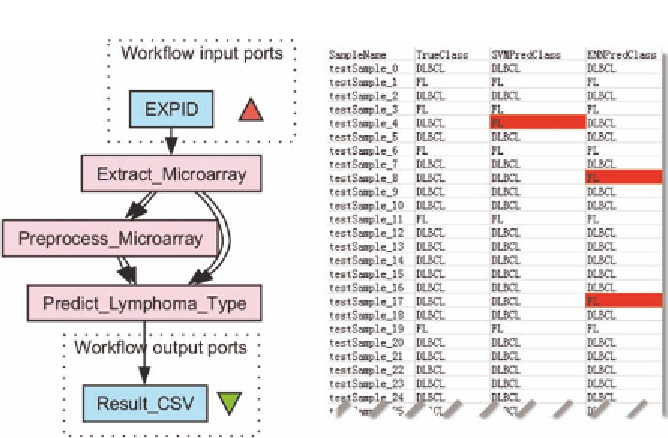
Figure 7.10
Lymphoma type prediction workflow and the result. Microarray data are
extracted from caArray, preprocessed, and used to learn a model for lymphoma type
prediction. The result is a csv file describing the actual lymphoma type of each tumor
sample and the prediction results using SVM and KNN algorithms, respectively.
starts with the extraction of hybridization data from a given experiment
in the aforementioned caArray database (nested workflow
Extract_
Microarray
).These hybridizations are from tumor samples that belong
to two different lymphoma types, i.e., diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
(DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). Next, the hybridization data
are preprocessed (nested workflow
Preprocess_Microarray
) and then
used to learn a classification model using two machine learning
methods, i.e., support vector machine (SVM) and
K
-nearest neighbor
(KNN). This model is used for lymphoma type prediction when an
unknown sample comes in (nested workflow
Predict_Lymphoma_
Type
). The type prediction result is shown in the right part of Fig-
ure 7.10.
SampleName
represents different tumor samples;
TrueClass
is
the lymphoma type obtained by manual investigation (and is considered
to be accurate); and
SVMPredClass
and
KNNPredClass
represent the
types predicted by SVM and KNN, respectively. Prediction errors are
highlighted. While Figure 7.10 shows the skeleton of the lymphoma
workflow by condensing the nested workflows, Figure 7.11 gives a
detailed view with nested workflows expanded.