Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
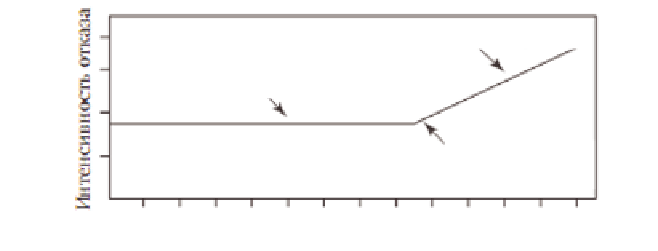
Increase as a result of ageing
Failure rate
Time to start of
ageing
Time (years)
2.1
Scheme of evaluation of the probability of failure during operation.
component of equipment of nuclear power plant
26
. A linear model of ageing
was used in this case. As shown in Ref. 25, it is necessary to determine
two parameters from the operational statistics:
• failures associated with ageing;
• constant failure rate, when ageing is absent (Fig. 2.1).
The approach described can also be used with a non-linear dependence of
reduction of reliability due to ageing (or time of operation). It simplifies the
method for using the existing performance data. However, as shown in Refs.
16, 28, etc, such an approach has proved fruitful for the active elements of
nuclear power plants. For mechanical elements (equipment, piping, etc.) it
is complicated to use the above-mentioned simple models. This is due to:
1. Lack of sufficient information which can be subjected to statistical
analysis.
2. Low quality of available information, which often lacks detailed
description of failure and cause of the defect, the reasons for failure, etc.
3. Scatter of data for various nuclear power plants and the lack of
an uniform data collection system. In this regard, a task of developing
a data collection system and use it to study ageing and the prediction of
reliability and safety with ageing taken into account was formulated within
the framework of OSCE. 14 countries take part in the programme.
4. The disadvantage of the above models is also that the conditions of
the transition of the defects from the monotonic, quasi-static process to
the process of rapid, almost instantaneous destruction are not taken into
account.
2.2 Markov processes
It is very convenient to describe the appearance of random events in the form
of transition probabilities from one state of the system to another, since it is
assumed that by going to one of the states the system should not continue
to consider the circumstances of how it came to this state.
A random process called a Markov process (or
process without
aftereffect
), if for every moment
t
the probability of any state system in
Search WWH ::

Custom Search