Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Relative length of defect
c
/(π
R
)
9.28
Longitudinal orientation of the crack. Improved accuracy of
the results:1) operating mode; 2) emergency mode; 3) hydraulic
tests; 4) operating mode, experimental data
89
; 5) emergency mode,
experimental data
89
; 6) rejection level.
Q
, l/h
HT
NOC
2
c
, mm
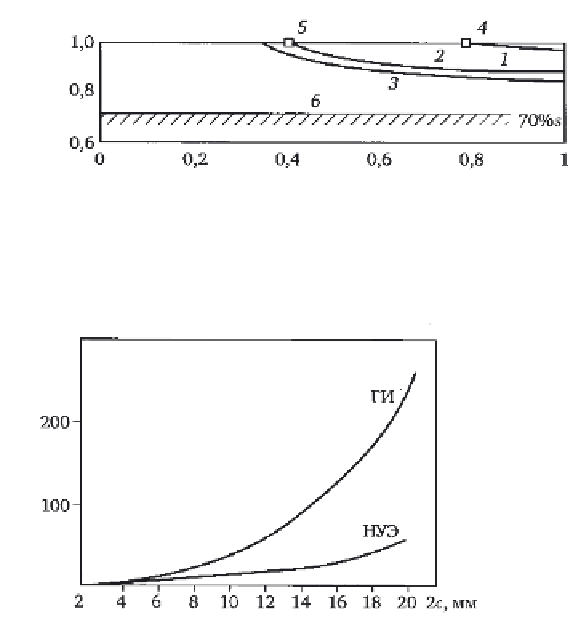
9.29
Dependence of the flow rate of water
Q
on the length of a
continuous crack 2
c
.
contain relatively large through-wall cracks due to the relatively low
thermomechanical loading of the HETs.
The results of the calculation of leakage through the through-wall cracks
are shown in Fig. 9.29.
A continuous longitudinal crack with length 2
c
in the internal wall of a
pipe was investigated. The calculation procedure is described in Ref. 138.
The calculations took into account the form factor of the crack and the
effect of roughness of the crack edges on jet suppression. The calculations
were performed for two modes: for normal operating conditions (NOC) and
hydraulic tests with the pressure of
p
HT1
= 24.5 MPa and
p
HT2
= 0.
It is common knowledge that control of SG boiler water radioactivity
allows to seal leakages (about 1 l/h) from the primary to secondary
circuit. When a leak of about 3 l/h is detected, a shutdown is considered. At
the same time, the limiting size of a leak from the primary to secondary
circuit shall not exceed 5 l/h.
The results of calculation of the coolant flow through a continuous
longitudinal crack in HETs showed that in the NOC mode the coolant flow


Search WWH ::

Custom Search