Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
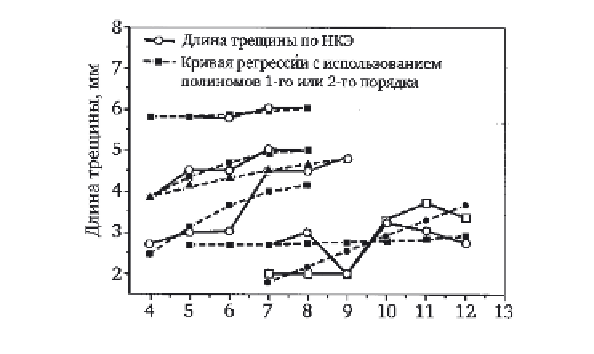
Crack length according to NIS
The regression curve plotted using the
polynomials of the first or second order
Number of inspections
9.14
Description of data on crack length by polynomials.
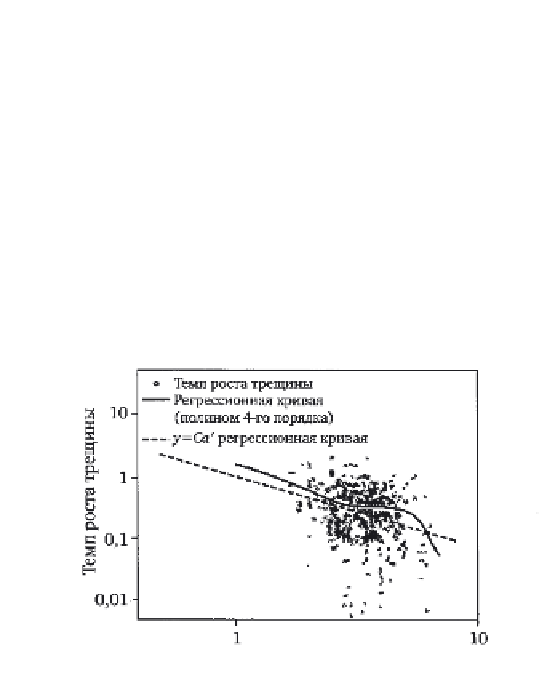
Crack growth rate
Regression curve (polynomial of the
fourth order)
y
=
Ca
' regression curve
Crack length, mm
9.15
Regression analysis of the crack growth rate.
between the length of the crack and its growth rate, using a fourth degree
polynomial. The results show that the growth rate decreases with increasing
crack size. This pattern is consistent with earlier data
128
.
As expected, the crack growth rate satisfies the following equation [127]:
da
dt
=
faz
(),
[9.1]
where
a
is the crack length,
t
is time,
f
(
a
) if the function of crack length
a
,
and
z
is
a
statistical random variable, taking into account the random error.
One of the simplest forms of equations [9.2] is as follows:
da
l
=
Ca z
,
[9.2]
dt
where
C
and λ are constants. Logarithmic transformation of both sides of the
equation [9.2] leads to the following:



Search WWH ::

Custom Search