Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
8.3 Optimisation of the technical inspection and
scheduled preventive maintenance
8.3.1 Optimisation of scheduled-preventive
maintenance
Optimisation of scheduled-preventive maintenance (SPM) using probabilistic
methods of structural strength can be performed on the basis of both the
composition of and periodicity of operations.
The simplest approach is to monitor the actual level of reliability
of components and pipes which are important for safety. SPM of these
elements should be carried out on the basis of the criterion of reaching an
unacceptable level of reliability.
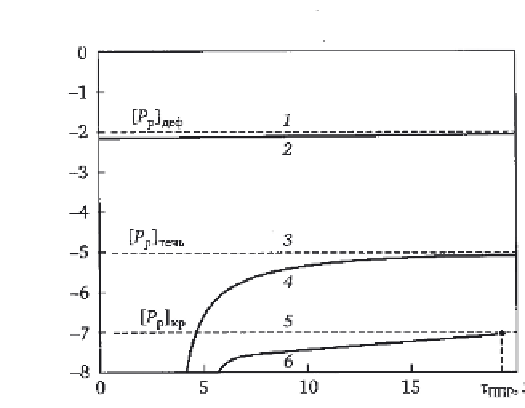
Figure 8.16 shows schematically the change in the probability of the
existence of discontinuities with the unacceptable size in equipment in
operation (curve 2), the probability of leaking (curve 4) and the probability
of failure of the structural element (curve 6). SPM should be carried out
when unacceptable values of probabilities are recorded.
The case of expulsion from the SPM of eddy-current testing of tubes of
steam generators reactors VVER-440, units 3 and 4 of the Novovoronezh
NPP, is described in section 9. The volume of these operations was
reduced on the basis of analysis of the reliability of the tubes which, after
lg
P
f
(τ)
[
P
f
]
def
[
P
f
]
leak
[
P
f
]
cr
τ
SPM
, years
8.16
Time of next scheduled-preventive maintenance determined
using the reliability characteristics on the basis of the criteriaof
maximum detectability of unacceptable discontinuities in operation
lg
P
f
(
τ
) (curve 1 - normative and 2 - actual), the maximum probability
of leakage (curve 3 - regulatory and 4 - actual) and the maximum
probability of failure (curves 5 - regulatory and 6 - actual).



Search WWH ::

Custom Search