Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Volume
7. 6
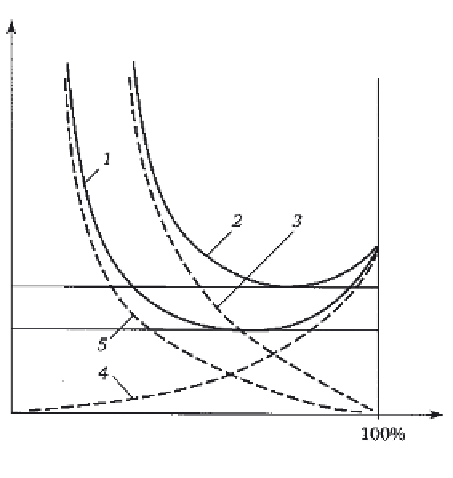
Relationship between ISI and its cost: 1) total cost in 'good'
(correct) selection of inspection volume; 2) total cost at 'poor'
(incorrect) selection of inspection volume; 3, 5) cost for nuclear
power plant; 4) cost of ISI.
is displaced to the right and to a higher level (i.e. will increase) at which
the minimum total cost of less effective inspection may well be greater
than the total value of effective inspection. Thus, the higher the efficiency
of the ISI, the larger the volume of inspection that can be substantiated
and verified.
However, the radiation doses received by staff even with effective
inspection are a limiting factor restricting the inspection volume. In-
service inspection, based on risk information, offers a flexible approach to
reduce radiation doses. In the case where several areas of inspection with
the same level of risk are assessed for inclusion in the inspection volume,
it is recommended to give preference to regions with the lowest possible
radiation exposure. Consequently, the given level of risk can be achieved
at the lowest dose rates.
Such a comprehensive concept that takes into account all factors
affecting the cost and safety, considering the real value of inspection,
should be used in developing standard programmes for ISI of equipment
and piping, components and structures of nuclear power plants.
The relationship between the frequency of the ISI and its effectiveness
should be supplemented in the light of the concept of inspection based on
risk information.
As described in Ref. 110, the determination of the operating life of
the component and the time periods between inspections can be shown
schematically in the probabilistic aspect taking into account the required
Search WWH ::

Custom Search