Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
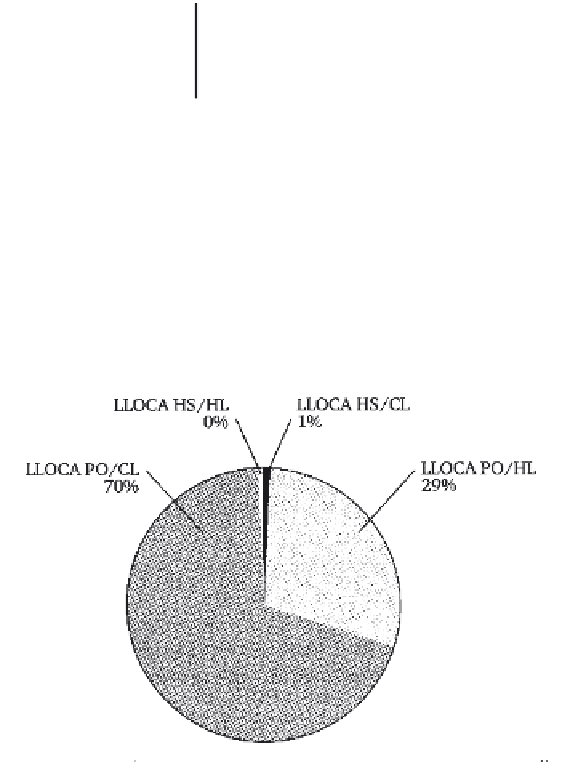
Table 6.1
Distribution of risk in relation to the location of the leak and the
state of the reactor
Contribu-
tion to
total risk of
TRMS
IE
frequency
IE
IE code
CDF
Large leak from hot loops,
power operation
2.05 ·
10
-8
LLOCA PO /HL
1.61 · 10
-5
29
Large leak from cold loop
power operation
5.03 ·
10
-8
LLOCA PO /CL
2.41 · 10
-5
70
Large leak from the hot loop,
hot shutdown
3.34 ·
10
-10
LLOCA HS /HL
1.79 · 10
-7
> 0.5%
Large leak from cold loop and
hot shutdown
7.21 ·
10
-10
LLOCA HS /CL
2.68 · 10
-7
1
7.18 ·
10
-8
Total
4.06 · 10
-5
6.2
Main factors causing core melt under large-break LOCA.
Analysis of minimal cross sections (see Table 6.3) determines the most
significant failures of system components and erroneous personnel actions,
leading to reactor core melting. Large-break LOCA accidents include:
• in the AS 3 ET LLOCA PO/CL (leak from the cold loop, reactor at
power),
- failure to open the check valves on the injection lines into the cold
loop (21% of the total risk of CDF);
- common cause failures of emergency pumps make-up pumps (7% of
the total risk);
- failure of the control system for automatic switching to recirculation
through the sump due to human error when setting four relays (5% of the
total risk of CDF);











































Search WWH ::

Custom Search