Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
DDP
a)
CRP
b)
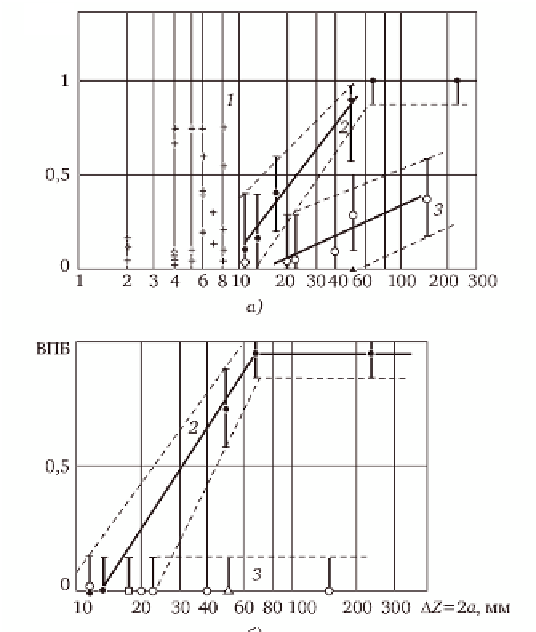
5.21
The main results of PISC-I: a) defect detection probability
(DDP), depending on the size, b) correct rejection probability
(CRP) of defects depending on their size; + - permissible defects;
• - unacceptable defects (vertical cracks); o - chains of defects;
,
Δ - difficult to detect defects because of their location; 1) bulk
defect; 2) crack-type defect, 3 - chains defects.
improved, but not enough to consider the results satisfactory.
Following the PISC-II programme, the PISC-III programme was
developed. This programme covers a wider range of problems associated
with the reliability of NDIS. Eight areas of work were proposed:
Direction 1
(real deactivated structural elements) provided the study of
reliability of inspection for the decommissioning of damaged elements of
the reactor structures.
Direction 2
(inspection on a full-scale model of the reactor pressure
vessel) is a direct continuation of PISC-I, PISC-II programmes but this time
the study was as close as possible to the real conditions. The main volume
of work was conducted at the Institute for Testing and Materials in Stuttgart
(Germany). The full-scale model of the reactor provided an opportunity to
test the robotic arms for NDIS of reactor casings.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search