Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
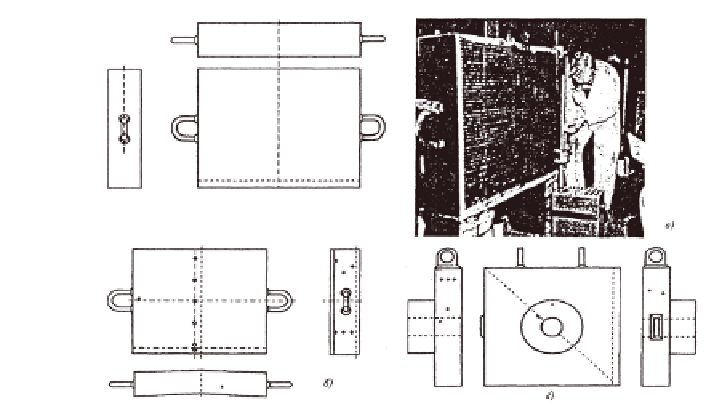
d)
a)
b)
c)
5.20
Test samples for PISC-I: a) plate no. 51/52; b) plate no. 51/53;
c) view of the sample, d) nozzle 204.
• quality and errors in determining the location of the defect:
• quality and errors in determining the linear dimensions of the
defects;
• probability of making correct or incorrect decisions on the basis of
the inspection results accordance with the ASME (XI) rules.
The main results obtained within the framework of PISC-I are shown in
Fig. 5.21. These results indicate that the reliability of NDT is unacceptable
for nuclear engineering. It was shown experimentally that the probability
of making wrong decisions in the analysis of test results is very high. In
some cases, for example, for chains of defects it is actually equal to 100%.
In connection with the results, methods alternative to the ASME (XI)
code were introduced to the PISC-I programme. The results obtained by
additional methods were significantly better, but it was decided to continue
research under the programme PISC-II.
The purpose of the PISC-II programme was the following:
• assessment of the effectiveness of various alternative methods of
inspecting the elements of reactors in operation;
• define procedures acceptable for input inspection, preoperational
and operational inspection;
• bring to the attention of supervisors the results of research and
develop normative and technical documents (rules, standards) on
the basis of these results.
One of the generalised results of studies of detection of defects produced
by PISC-II is shown in Fig. 5.22. It can be seen that the detection of
fatigue cracks and chains of fissures in the investigations has been greatly


Search WWH ::

Custom Search