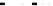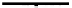Database Reference
In-Depth Information
databases without the integrity constraints which can make this schema inconsistent.
In what follows, we consider that by using such strategies, we guarantee that the
insertion of the information from another databases in
G
into a given schema always
produces a new model (instance-database) of this schema.
Consequently, the process of the updates propagates from
A
into
B
and hence
may continue to propagate from
B
to another database schemas in
E
G
(a forward
chaining propagation in
G
).
Hence, we may see this transition
α
∗
==
M
AB
⇒
α
1
as a
DB-atomic transition
of an
LTS that represents the complete process of a forward chaining. In the case when
G
is not an acyclic graph, the tree of this LTS can be infinite as well (in the case, for
example, when we use the full tgds for inter-schema mappings, so that
(q
A
i
(
x
i
)
⇒
∃
∈
M
AB
, and in the place of tuple of variables
y
i
we insert the new
Skolem constants).
Let
r
I
i
be the relational symbol for the set of tuples in
t
i
⊆
y
i
q
B
i
(
x
i
,
y
i
))
=
t
i
,for
i
1
,...,n
,
(V
i
,t
i
)
. It is easy to show, based on case 2 of Example
34
and Definition
50
,
that this atomic transition
α
∗
===
∈S
B
M
AB
⇒
α
1
, which represents the inserting of tuples
in the
k
by the inserting operations
'INSERT INTO
r
i
...
', with
r
I
i
a relation to be inserted,
i
=
n
relations of the database
B
,
r
1
,...,r
k
∈
B
=
1
,...,k
, can be rep-
α
∗
(
α
1
(
resented in the
DB
category as the morphisms
f
I
=
B
:
B
→
B
)
.
This morphism in
DB
is represented as a horizontal arrow from the instance
database
B
=
α
∗
(
B
)
in the diagram on the left ellipse, which represents the image
of the data mapping graph
G
for the initial interpretation
α
∗
, into the new updated
instance
α
1
(
η
P
n
◦···◦
P
1
(
)
)
in the diagram on the right ellipse (which represents
the image of the data mapping graph
G
for the resulting interpretation
α
1
).
Note that the enlarged horizontal arrow represent the satisfied morphism in
DB
while the enlarged vertical arrows is satisfied arrow of a database mapping graph
G
if
t
i
=
t
i
for all
(V
i
,t
i
)
∈S
B
B
)
of a schema
B
.
This
forward propagation
is denoted by the cone of arrows from the node
(schema)
A
in the diagram above).