Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
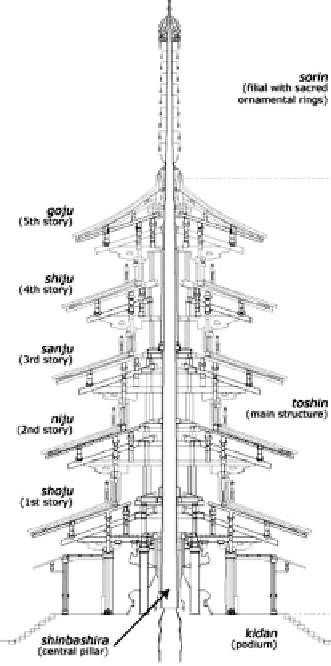
Fig. 5.5 Section through
a five-tier pagoda.
http://
small number of such wooden structures to survive in Japan (very few additional
examples can be found in China and Korea). The survival of pagodas of this type
(there are three-tier pagodas of similar design), while so many other contemporary
and later structures were destroyed by earthquakes over the years, is wondrous. It
begs a look into the structural properties that made them withstand the harsh jolts
they had suffered more than once. Figure
5.5
shows the structure to consist of five
stories that are arranged around a central pillar, shin-bashira, which protrudes
beyond the top of the fifth story to crown the pagoda with a symbolic ornamental
top, Sorin.
Nakahara et al. (
2000
) explain that structurally, three features stand out in the
pagoda: First, the central pillar does not have a foundation in the ground, as
one would normally expect; it just rests on the base stone in the podium. Second,
the five stories are also not attached to the ground or to each other; each story rests
on the previous one and encircles the central pillar, without being connected to
it. Third, each story is constructed of wooden members that are connected to one
another with many complex joints. Japanese wooden construction is famous for its
Search WWH ::

Custom Search