Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
MERCURE
SPRAY
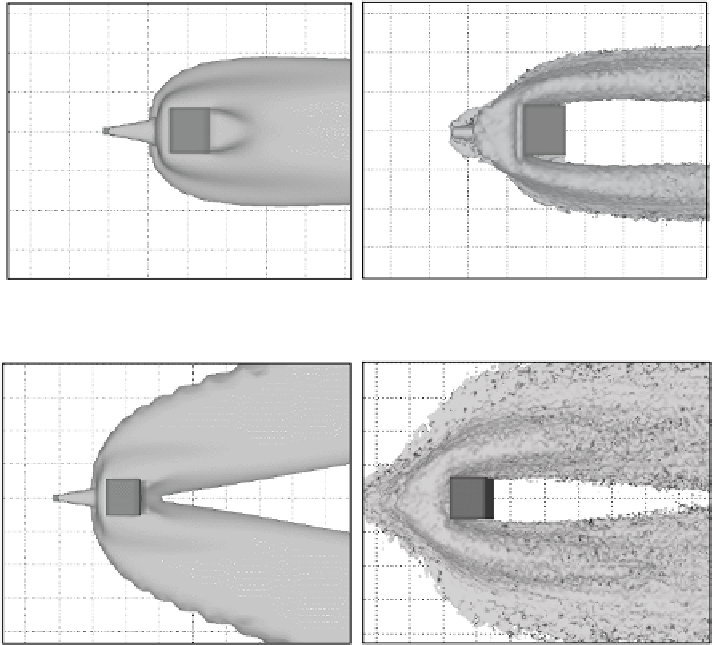
Fig. 1.
Neutral gas: concentration mixing ratio, iso-surface 0.01 kg/kg obtained by Mercure (left)
and MSS (right)
MERCURE
SPRAY
Fig. 2.
Dense plume: concentration mixing ratio, iso-surface 0.01 kg/kg obtained by Mercure
(left) and MSS (right)
MSS estimates more 'counterflow' motion than Mercure in both cases, but
the effect of the ground spread is more enhanced with dense gas, as expected. In the
neutral gas emission, the plume in MSS splits downwind the obstacle, while the
same iso-surface keeps non-zero values for Mercure, due to the different level of
turbulence Generated by the CFD model in the lee of the obstacle. In the dense gas
emission experiment both Mercure and MSS show an evident splitting of the plume
at ground, and a large horizontal spread due to the gravity effects. Qualitatively,
the two models show a similar behaviour of the plume. Analogous numerical
experiments are under process for jet emission of light gases.
4. KIT FOX Simulations
The 1995 Kit Fox dense gas field data set (Hanna et al., 1991) consists of 52 trials
where CO
2
was releases from a 1.5 × 1.5 m ground level source over a rough