Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3. Results and Discussion
Aged air masses usually contain increased numbers of CCN. For the greater
Mediterranean area, CCN are often composed of a mixture of several species
such as sulphate coated or salt coated mineral dust particles, sea-salt particles and
secondary particles from anthropogenic pollutants [8]. Such particles exhibit
higher hygroscopicity and play important role in cloud formation and precipitation.
The cloud droplet activation parameterization in ICLAMS is properly designed for
air-quality applications since it allows the aerosol species to explicitly interact
with the model physics and dynamics. Proper handling of aerosol properties and
aerosol-cloud interactions in the model leads into remarkable improvement in
precipitation estimation
(Fig. 1)
and consequently in wet deposition and air quality
analysis (
Fig. 2).
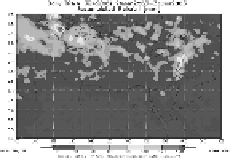
Fig. 1.
120 h accumulated precipitation (mm) (26-31January 2003). (a) TRMM Satellite
observations (b) model results with aerosol meteorology interaction and (c) model results
without aerosol meteorology interaction
a
c
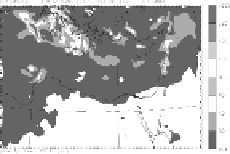
Fig. 2.
120 h model accumulated dust wet deposition (mg/m
2
) (26-31 January 2003). (a) Aerosol
particles are treated as passive tracers. (b) Aerosol meteorology interaction
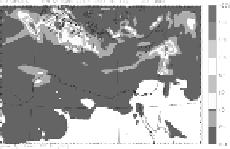
When utilizing aerosol chemistry, the sulfates are higher in the areas where
there are significant emissions of SO
2
and slightly smaller when the SO
2
availability is limited (
Fig. 3a).
This is a result of the formation of additional
aerosols from H
2
SO
4
which depends on SO
2
. The SO
2
concentrations are lower in
the presence of clouds when the aerosol module is utilized (
Fig. 3b).
This happens
due to the adjustment of the gas and vapor phase concentrations of SO
2
in order to
be in equilibrium with the aerosol phase. The available SO
2
in the atmosphere
reacts with hydroxyl radical to produce HO
2
and sulfates. Hence it is an indicator