Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0.5 km horizontal grid spacing. In this study we consider several typical synoptic
conditions for Israel (Alpert et al., 2004; Osetinsky, 2006); a summer case will be
discussed in this abstract. On August 2008 a campaign of high resolution upper air
measurements was conducted. The purpose of the campaign was to obtain upper
air data for validating the model results, along with ground stations data. GPS
radiosondes were launched from three sites: two in Haifa Bay and one on Mt
Carmel at different hours (up to three times a day). Results of RAMS simulations
were compared with these measurements.
2. Methodology
The high resolution radios
ondes w
ere tracked up to 5,000 m, recording tempe-
rature, pressure, relative humidity and wind. Data was averaged over 50 m layers,
reducing some noise of the measurements (especially of the wind). RAMS was
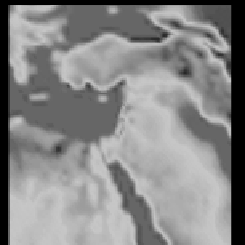
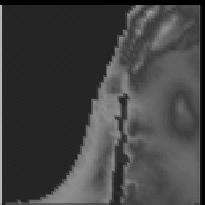
run with four nested grids (Fig. 1), ranging from the synoptic scale initiated with
NCEP reanalysis data, down to the urban scale. The model was tested for several
configurations; some of the current results are shown here.
The model results were compared with data from the monitoring network
observations of the Israeli Meteorological Service, as well as with observations
from Haifa District Municipal Association for the Environment (“Igud”) and with
the measured high-resolution upper air profiles.
Nested Grids
Nested Grids
G4 res. 0.5km
G4 res. 0.5km
G1 res. 32km
G1 res. 32km
G2 res. 8km
G2 res. 8km
G3 res. 2km
G3 res. 2km
Fig. 1.
RAMS four nested grids used for the simulations