Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
increasing
with depth
• boron
• salinity
• water
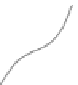
Fig. 15.7
Most soils containing high concentrations of boron are also affected by salinity and
low rainfall. Boron and sodium concentrations usually increase down the soil profile which has
an inhibitory effect on roots trying to access subsoil moisture. The effect of cellular boron toler-
ance mechanisms on the pattern of development of roots early in the growing season, may have
positive or negative impacts on late season growth and yield. (Reprinted from Reid (
2009
) with
permission)
growth is not well understood, and we can only confidently say that it is important
in stabilising cell walls. On a more positive note, the past decade has provided us
with some excellent insights into the functioning of boron transporters and their im-
portance in avoidance of boron deficiency and toxicity. This is likely to be a fertile
area for further research. The recent discovery of a boron tolerance mechanism not
related to boron transport suggests that internal tolerance does exist and might be
exploited.The quest for crop plants that can tolerate high levels of soil boron will no
doubt continue but has been made more difficult by the need to consider the effect
of associated stresses such as drought and salinity.
References
Alpaslan M, Gunes A (2001) Interactive effects of boron and salinity stress on the growth, mem-
brane permeability and mineral composition of tomato and cucumber plants. Plant and Soil
236:123-128
Avci M, Akar T (2005) Severity and spatial distribution of boron toxicity in barley in cultivated
areas of Central Anatolia and Transitional Zones. Turkish J Agric For 29:377-382
Ashworth LJ. Jr, Gaona SA, Surber E (1985) Nutritional diseases of pistachio trees: Potassium
and phosphorus deficiencies and chloride and boron toxicities. Phytopathology 75:1084-1091
Bassil E, Hu H, Brown PH (2004) Use of phenylboronic acids to investigate boron function in
plants. Possible role of boron in transvacuolar cytoplasmic strands and cell-to-wall adhesion.
Plant Physiol 136:3383-3395
Ben-Gal A, Shani U (2002) Yield, transpiration and growth of tomatoes under combined excess
boron and salinity stress. Plant and Soil 247:211-221
Bingham FT, Strong JE, Rhoades JD, Keren R (1987) Effect of salinity and varying boron concen-
tration on boron uptake and growth of wheat. Plant and Soil 97:345-351