Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
3KHQ\O3URSDQRLG3DWKZD\
6KLNLPLF$FLG3DWKZD\
$QWKRF\DQLQV
)ODYRQHV)ODYDQROV,VRIODYDQRLGV
7DQLQV
&KRULVPLFDFLG
7ULWHWUDK\GUR[\
FKDOFRQH
,&6
,VRFKRULVPLFDFLG
6$
PDORQ\O&R$
/LJQLQ
ELRV\QWKHVLV
3/
$URJHQLFDFLG
3KH
SFRXPDUR\O&R$
3$/
7\U
0H6$
7UDQVFLQQDPLF
SFRXPDULFDFLG
DFLG
2FRXPDULFDFLG
&
+
%HQ]RLF
DFLG
)UHH6DOLF\OLFDFLG
526
6$
+
2
/RFDO5HVLVWDQFH
6$
-
*OXFRVLGH
'%+$
'%+$
6\VWHPLF$FTXLUHG5HVLVWDQFH
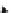
Fig. 6.2
Correlation of SA biosynthesis with phenylpropanoid pathway and elicitation of local and
systemic defense (
ICS
isochorismate synthase;
PL
pyruvate iyase;
Pal
phenyl ammonium lyase;
GTase
3-O-glucosyltransferase;
DBHA
dihydroxybenzoic acids;
C
4
H
cinnamate 4-hydroxylase;
and
Try
tyrosine)
3.1 Microbial Challenge and SA Upsurge in Tissues
Earlier studies have revealed the major role of SA in counteracting the biotic stress
responses in plants. White (
1979
) first evidenced the involvement of SA in plant
defense mechanism. Internal increase in SA levels during pathogenic plant-microbe
interaction often facilitates the building-up of the resistance and SAR (Ryals et al.
1996
). SA induces resistance against many necrotic or systemic viral, bacterial and
fungal pathogens in a variety of plants (Weete
1992
; Malamy and Klessig
1992
).
Durrant and Dong (
2004
) clearly reviewed the demonstration of SA accumulation
and its subsequent role in signaling, by using mutant and transgenic plants. En-
dogenous SA protects plant from oxidative damage either through aging, abiotic
stress or biotic stress (Yang et al.
2004
). Bacterial SA degrading enzyme
salicylate
dehydroxylase
(
NahG
) when over-expressed in transgenic
Arabidopsis
and tobacco
plants, developed inefficient defense response and showed more susceptibility to
pathogen infection damage (Gaffney et al.
1993
; Delany et al.
1994
). Possibly, SA
inhibited pathogen growth by repressing the auxin signaling pathways in plants
(Wang et al.
2007
). Evidence shows that the manipulated host auxin-biosynthesis
takes place through interference in normal developmental process (Dharmasiri et al.
2005a
,
b
; Kepinski
2005
). Plants probably themselves repress auxin signaling to
come up with defense strategy during infection although many pathogens them-