Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
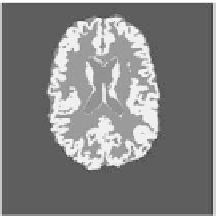
Figure 4.
Some 2D displays of segmentation results (into WM, GM, CSF). Slice 69 from
MRI scan of (a) an 68-year-old autistic female; (b) a 4-year-old autistic male; (c) a 34-year-
old healthy male. See attached CD for color version.
Figure 5.
Distance map concept. See attached CD for color version.
centered at each point and cover its entire nearest neighbors. In 2D space, two
stencils cover the 8-neighbors of the point as shown in Figure 6. For those stencils
that are not aligned with the natural coordinate system, the eikonal equation is
derived using directional derivatives and then solved using a higher-order finite
difference scheme [66]. Figure 7 shows the distance maps inside the segmented
white matter corresponding to two 2D typical slices from the postmortem data at
hand. These distances were computed using the proposed method MSFM.
In order to use the distancemap,
D
(
·
), of a given object, Ω
1
as a discriminatory
Ω
2
, and we compute the
CumulativeDistribution Function (CDF) of
D
(
·
) inside of Ω
1
and compare it to that
feature that distinguishes it from other objects, e.g.,