Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
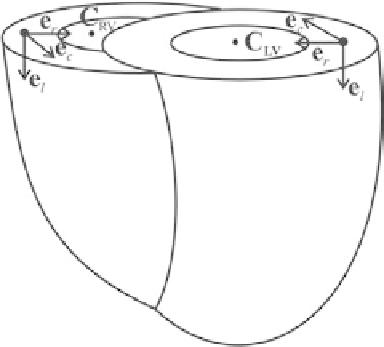
Figure 9.
Strain calculation directions for both the left and right ventricles given by the
orthonormal basis
{
e
r
,
e
c
,
e
l
}
. The centers of the left and right ventricles are shown by
the points
C
LV
and
C
RV
, respectively.
Directional strains are calculated and regionally averaged based on myocardial
geometry consistent with clinical reporting [29]. The recommendation presented
divides the left ventricle into seventeen regions. The division along the midven-
tricular axis consists of four layers: basal, mid-cavity, apical, and apex. The top
three layers (basal, mid-cavity, and apical) encompass the endocardial cavity re-
gion. Based on the locations of the LV/RV junctions, the basal and mid-cavity
portions of the left ventricle are each further divided into six regions in the short-
axis view: antero-septal, anterior, lateral, posterior, inferior, and infero-septal.
Similarly, the apical portion is divided into four regions anterior, lateral, inferior,
and infero-septal. The apex comprises the seventeenth region. We follow the di-
vision utilized in [5] for regional analysis of the right ventricle. Similar to the left
ventricle, the right ventricle is divided into basal, mid-cavity, and apical layers.
Each layer is further divided into anterior, mid, and inferior regions.
The orthonormal basis for calculating directional strain is given by
{
e
r
,
e
c
,
e
l
}
(Figure 9).
C
LV
, used to calculate directional
strain values, is the same point as the origin of the coordinate system calculated
from the center of the short-axis endocardial contour of the most short-axis basal
image slice.
The center of the left ventricle,
C
RV
is derived from the right-ventricular NURBS model for each
w
RV
parametric value by fitting a circle to the curve of constant
w
RV
value with
u
RV
=0
.
5. As this process is dependent upon the curvature of the right ventricle,
it is possible that
C
RV
is not inside the right-ventricular cavity. However, this is
not important since
C
RV
is only used to derive the orthonormal basis
{
e
r
,
e
c
,
e
l
}
for calculating the right-ventricular normal strains.