Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
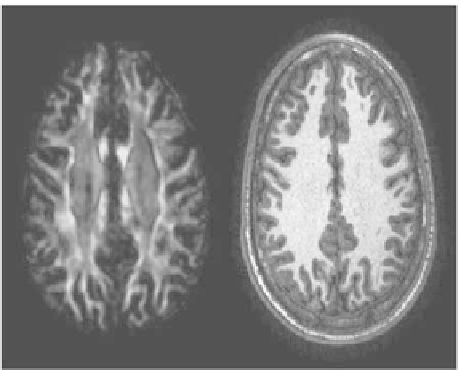
Figure 2.
A diffusion tensor image that shows the white matter bundles and the corre-
sponding MRI slice. See attached CD for color version.
multiple sclerosis and dyslexia). Recently, Lenglet et al. [21] proposed a global
approach to white matter connectivity mapping through global modeling of the
white matter as a Riemannian manifold, and used the diffusion information to
infer its geometry and compute its geodesics, which correspond to diffusion path-
ways. The level set method was used in that work to compute the signed distance
and for geodesic estimation. Goraly et al. [25] conducted a study to investigate
the values of the fractional anisotropy of the DTI in seven autistic children.
Some studies have been conducted to analyze developmental dyslexia through
Diffusion Tensor Imaging [26], but we propose a novel method to investigate DTI
in analyzing dyslexia by analyzing the fiber tracts of the white matter in the outer
compartment and analyzing the relationship between the geometrical structures
of these fiber tracts that directly reflect the manner of communications between
minicolumns.
3.
PROBLEM STATEMENT, DATASET DESCRIPTION AND
PROPOSED APPROACH
One of the major causes of developmental disorders is that some parts of the
communication network of the brain fail to perform their tasks properly. Hence,
most of the previous MRI studies [2, 4, 5] focused on investigating morphometric
brain changes in certain structures such as the corpus callosum, brain stem, and
other structures. In this study we analyze the morphometric changes in the normal