Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
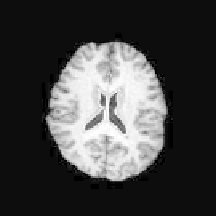
Figure 5.
Segmentation of lateral ventricles from MRI brain data: (a-c) final contour in
different axial slices; (d-f ) segmentation results represented by a 3D surface.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 6.
Segmentation of corpus callosum from 3D DTI data: (a) initial surface, a sphere;
(b,c) intermediate evolution results; (d) final result.
shown for the gray matter surface (Figure 7b), the white matter surface (Figure 7c),
and the cerebrospinal fluid surface (Figure 7d).
From Figures 4-7, we can see that our method can successfully delineate
brain tissues and the corpus callosum from 3D real images. The two-phase model
requires image preprocessing to obtain satisfying results. On the other hand, the
three-phase model can obtain very good results for scalped MR images. They both
demonstrate the potential of the proposed approach for medical image segmenta-
tion.